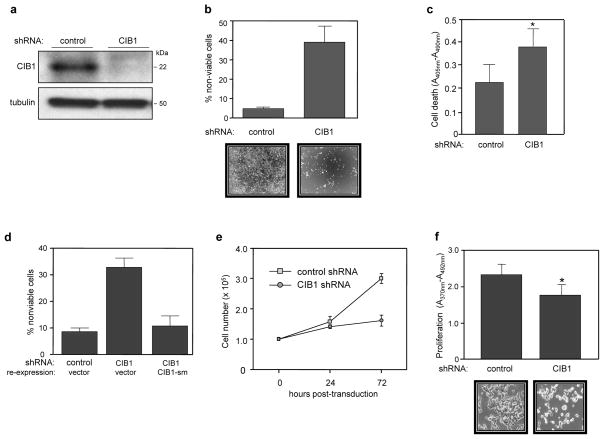
Figure 1. CIB1 depletion induces cell death and slows proliferation.
(a) Immunoblot showing efficient shRNA-induced CIB1 depletion from SK-N-SH cells. (b) Increased cell death in CIB1-depleted SK-N-SH cells as determined by trypan blue dye exclusion. Results are expressed as the mean percentage of dead cells (i.e., trypan blue positive cells) from both adherent and floating cell populations, data represent means +/− SEM, n=5. Representative phase contrast images show significant loss of adherent CIB1-depleted cells (bottom panels). (c) Analysis of control and CIB1-depleted SK-N-SH cells by immunochemical ELISA assays that detect histone-complexed DNA fragments as a marker of cell death (*p<0.05). (d) Ectopic expression of a shRNA-resistant CIB1 silent mutant (CIB1-sm) in CIB1-depleted SK-N-SH cells prevents cell death. Cell death was quantified as in (a), n=4. (e) Cell proliferation over 72 h, quantifed as total cell numbers at the indicated times post-transduction, n=2. (f) CIB1 depleted SK-N-SH cells show decreased cell proliferation as determined by BrdU proliferation assays (*p<0.05). Representative phase contrast images show significant loss of cell number from wells containing CIB1-depleted cells (bottom panels).