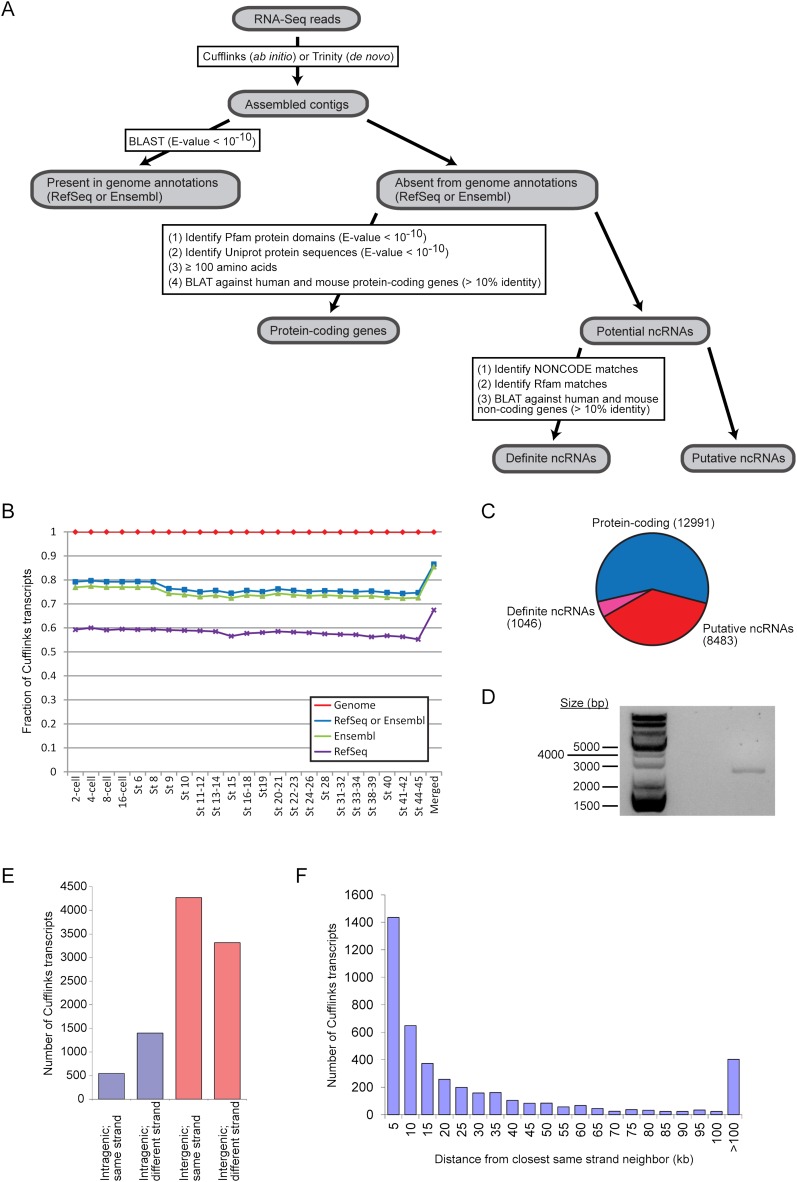
Figure 5.
Reconstruction of transcripts from RNA-seq data reveals novel transcribed regions. (A) Overview of our pipeline that defined a set of unannotated protein-coding genes and a set of novel noncoding RNAs. (B) Comparison of transcripts assembled by Cufflinks with the RefSeq (purple crosses) and Ensembl (green triangles) annotations as well as the reference genome (XenTro3, red diamonds). The blue squares correspond to Cufflinks transcripts that can be found in either the RefSeq or the Ensembl annotation. (C) A breakdown of the unannotated Cufflinks contigs into protein-coding transcripts and noncoding transcripts. (D) By reverse transcription PCR, we detected a gene product in the intergenic region between hoxc11 and hoxc12, where a long noncoding RNA, HOTAIR, is known to exist in mammals. The PCR product was further sequenced to confirm that it matched the correct genomic locus. (E) We classified the putative noncoding RNAs based on their genomic locations relative to annotated RefSeq or Ensembl genes. (F) For intergenic contigs that are on the same strand as one or both of their neighboring genes, we determined the distance of each Cufflinks transcript from its closest same-strand neighbor and binned the transcripts by this distance. In the histogram, “10 kb” means that the transcripts are between 9001 and 10,000 bp (inclusive) away from their same-strand neighbors and so on.