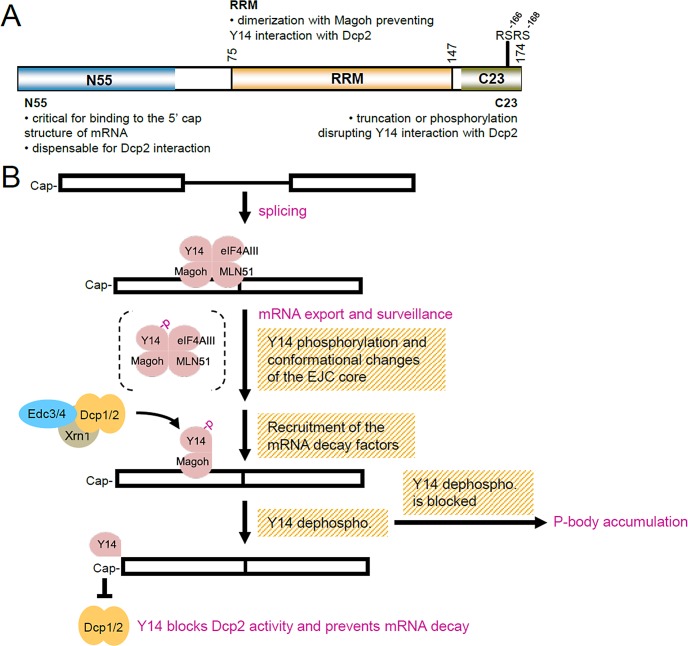
FIGURE 7:
Model of Y14 function in inhibition of mRNA degradation. (A) Schematic representation of the domains of Y14 and their functional roles in the inhibition of mRNA decapping. (B) A simplified model shows Y14 in postsplicing complexes and its possible role in the inhibition of mRNA degradation. Y14 associates with the EJC complex after pre-mRNA splicing and is exported with mature mRNAs to the cytoplasm and functions in NMD. Phosphorylation of Y14 may trigger its dissociation from the EJC/NMD complexes and allow the recruitment of the mRNA degradation factors. Subsequent dephosphorylation of Y14 activates its function in mRNA decapping. While dephosphorylation of Y14 is blocked, the mRNA degradation complex may accumulate in P-bodies.