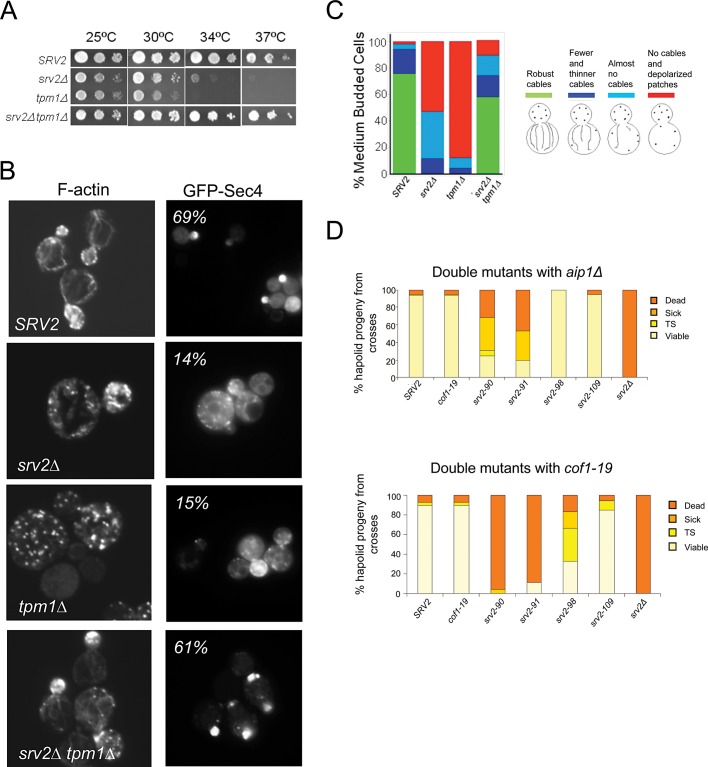
FIGURE 5:
Genetic analysis of N-Srv2 and C-Srv2 functions. (A) Suppression of tpm1Δ growth defects by srv2∆. Strains were grown to log phase, serially diluted, and grown on YPD plates for 2 d at 25°C, 30°C, 34°C, and 37°C. (B) Example images of cells grown at 25°C, fixed and stained with Alexa Fluor 488–phalloidin or showing GFP-Sec4 expressed from a low-copy plasmid in the indicated strains (Schott et al., 2002); percentage of cells with GFP-Sec4 predominantly in the bud listed in each panel (n > 100 cells). (C) Scored actin phenotypes of the same strains (n > 100 cells). (D) Genetic interactions of specific srv2 alleles with aip1∆ and cof1-19. Haploid srv2 mutants were crossed separately to aip1Δ and cof1-19. Diploids were sporulated, and tetrads were dissected (minimum: 20 tetrads, 80 spores). Resulting progeny were analyzed for cell growth at 25°C and 37°C. Shown are the percentages of haploid progeny that showed impaired growth at 37°C (temperature-sensitive, TS), grew poorly at all temperatures (sick), or did not grow at all (dead).