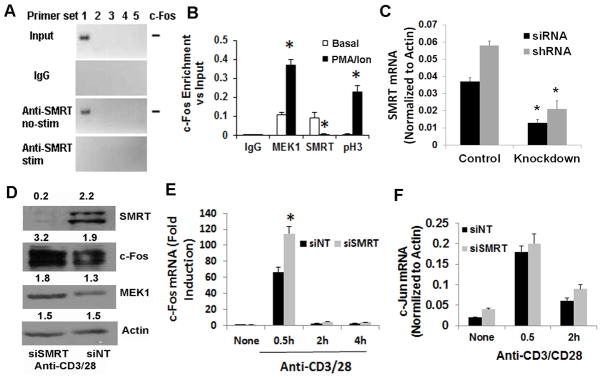
Figure 4.
A&B: ChIP studies with c-Fos promoter. CD4 T cells were stimulated (stim) with and without (basal) PMA (50 ng/ml)/ionomycin (1 μM). DNA was cross-linked to proteins using formaldehyde and sheared by enzymatic processing using the ChIP-IT Express Enzymatic kit. ChIP grade rabbit anti-MEK1, anti-SMRT and anti-phospho-H3 antibodies and control rabbit IgG were used to immunoprecipitate the bound chromatin. Following reversal of cross-linking and digestion of the proteins the DNA was used for PCR. Five sets of primers (#1 through #5 where #5 is proximal to the start codon site) were designed from the proximal promoter sequence of c-Fos and used in PCR. An image of the electrophoresed amplicons is shown in Figure A. The input DNA was electrophoresed at 1:50 dilution. The density of the bands generated with the #1 primer set was analyzed and presented as enrichment over the input. Results from 3 separate experiments are shown in Figure 5B. C: Expression of SMRT mRNA following siRNA- and shRNA-mediated knockdown. Purified CD4 T cells were either transfected with the Smartpool siRNA or infected with the shRNA retrovirus for SMRT. After resting overnight cells were stimulated with anti-CD3/CD28 antibodies for 30 min. Purified RNA was used for real-time PCR (N=3). D&E: CD4 T cells were transfected with siSMRT or control non-targeting siRNA (siNT) and stimulated as above for 0.5, 2 and 4 hr. An aliquot of cells that were stimulated for 0.5 hr was western blotted for SMRT, c-Fos, MEK1 and beta-actin (control) (D). The other aliquots were used to isolate RNA and real-time PCR for c-Fos (E) and c-Jun (F). N=3, *P<0.05, paired t test.