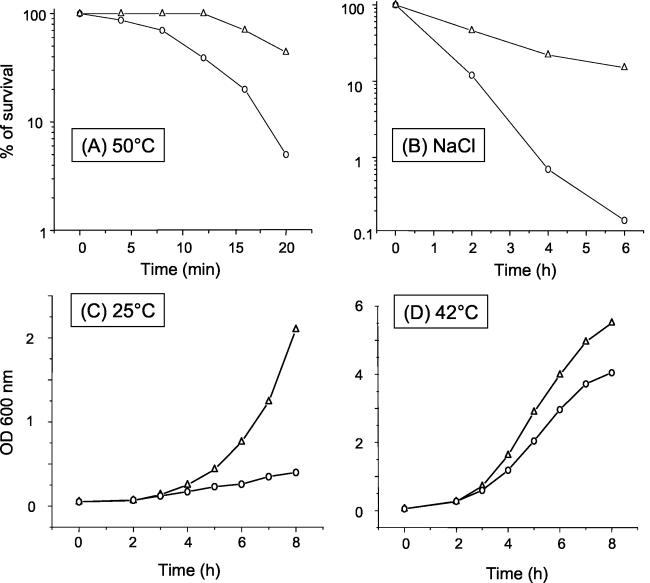
FIG. 5.
Resistance to temperature or osmotic stress and growth at different temperatures of the P. aeruginosa parental strain PT581 and mutant 19A. (A) To assay cell survival after exposure to heat shock at 50°C, stationary-phase cultures of PT581 (○) and 19A (▵) were grown in LB medium, washed in M9 medium, and transferred to prewarmed tubes. The number of viable cells in each suspension was measured by plating aliquots on LB plates at each time point and determining the number of CFU after overnight incubation. Viability is expressed as a percentage of the number of CFU at time zero. (B) To assay cell survival after exposure to 1.5 M NaCl, stationary-phase cultures of PT581 (○) and 19A (▵) were diluted in LB broth to an OD600 of 0.3, divided in two, and incubated with agitation at 37°C in the presence or absence of 1.5 M NaCl. Cell viability was determined after 2, 4, and 6 h. One hundred percent viability corresponds to the number of CFU present immediately after resuspension of the cells in 1.5 M NaCl. Heat and osmotic shock experiments were performed at least three times with reproducible results. (C and D) Growth curves of the P. aeruginosa parental strain PT581 (○) and mutant 19A (▵) at 25°C (C) and at 42°C (D) were performed in LB medium, and absorbance was measured at 600 nm. Growth experiments were performed three times.