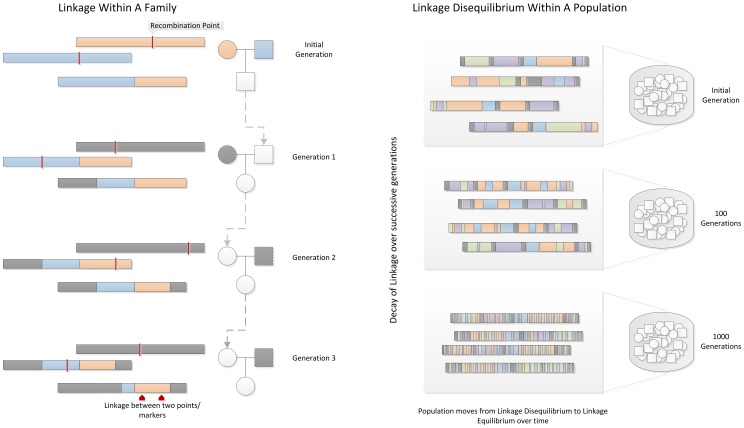
Figure 2. Linkage and Linkage Disequilibrium.
Within a family, linkage occurs when two genetic markers (points on a chromosome) remain linked on a chromosome rather than being broken apart by recombination events during meiosis, shown as red lines. In a population, contiguous stretches of founder chromosomes from the initial generation are sequentially reduced in size by recombination events. Over time, a pair of markers or points on a chromosome in the population move from linkage disequilibrium to linkage equilibrium, as recombination events eventually occur between every possible point on the chromosome.