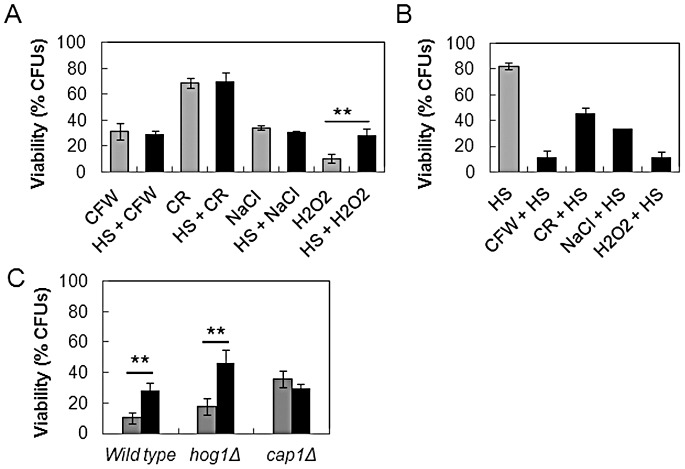
Figure 7. The cross-talk between thermal adaptation and cell wall stress resistance is not mediated via stress cross-protection.
(A) Stress cross-protection in C. albicans wild-type cells (NGY152: Table 1) was not observed for cells pre-treated with a heat stress and then subjected to cell wall stress, but was observed for cells exposed to a secondary oxidative stress. The data represent cell survival after exposure to a 30°C–42°C heat shock followed by a subsequent cell wall (CFW, CR), osmotic (NaCl) or peroxide (H2O2) stress (see Materials and Methods) and the data are expressed relative to unstressed cells (dark bars). Control cells (grey bars), were not exposed to the prior 30°C–42°C heat shock. (B) The reciprocal assay was performed, whereby C. albicans wild type cells were exposed to a prior stress (cell wall: CFW, CR; osmotic: NaCl; peroxide: H2O2) followed by a 30°C–42°C heat shock (dark bars). These data are expressed relative to unstressed cells. Control cells (grey bars) correspond to cells exposed only to the 30°C–42°C heat shock. (C) Wild type, hog1Δ (JC50) or cap1Δ cells (JC128: Table 1) were pre-treated with a 30°C–42°C heat shock, followed by a H2O2 stress (dark bars). Control cells (grey bars) were not exposed to the 30°C–42°C heat shock. The data represent the level of survival compared to unstressed cells. All data are the means from three independent assays: ** paired, two-tailed t-test, p<0.01.