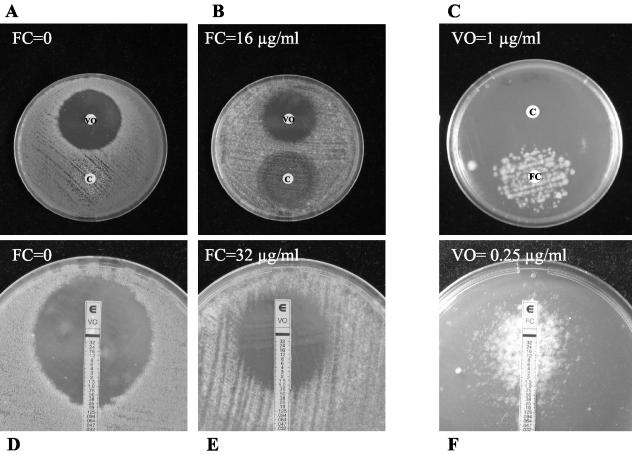
FIG. 1.
Agar diffusion test of the combination of flucytosine (FC) with voriconazole (VO) or caspofungin (C) against A. fumigatus AF2. (A and B) Paper disks impregnated with either 4 μg of voriconazole or 16 μg of caspofungin were placed on agar plates containing no antifungal (A) or flucytosine at 16 μg/ml (B). In the presence of flucytosine, the inhibition zone around the voriconazole disk decreased (indicating antagonism), whereas the inhibition zone around the caspofungin disk increased (indicating synergy). (C) Two paper disks impregnated with 16 μg of caspofungin (upper disk) or 128 μg of flucytosine (lower disk) were placed on an agar plate containing voriconazole at 1 μg/ml (concentration above the MIC). After incubation growth was apparent only around the flucytosine disk, indicating antagonism between voriconazole and flucytosine. Antagonism between caspofungin and voriconazole was not observed. (D and E) A voriconazole Etest strip was placed on agar plates containing either no antifungal (D) or flucytosine at 32 μg/ml (E). The voriconazole MIC increased from 0.19 μg/ml in the absence of flucytosine to 0.75 μg/ml in the presence of flucytosine, indicating antagonism between the two drugs. (F) A flucytosine Etest strip was placed on an agar plate containing voriconazole at 0.25 μg/ml (the MIC). After incubation an ellipse of growth was apparent around the strip, indicating antagonism between the two drugs.