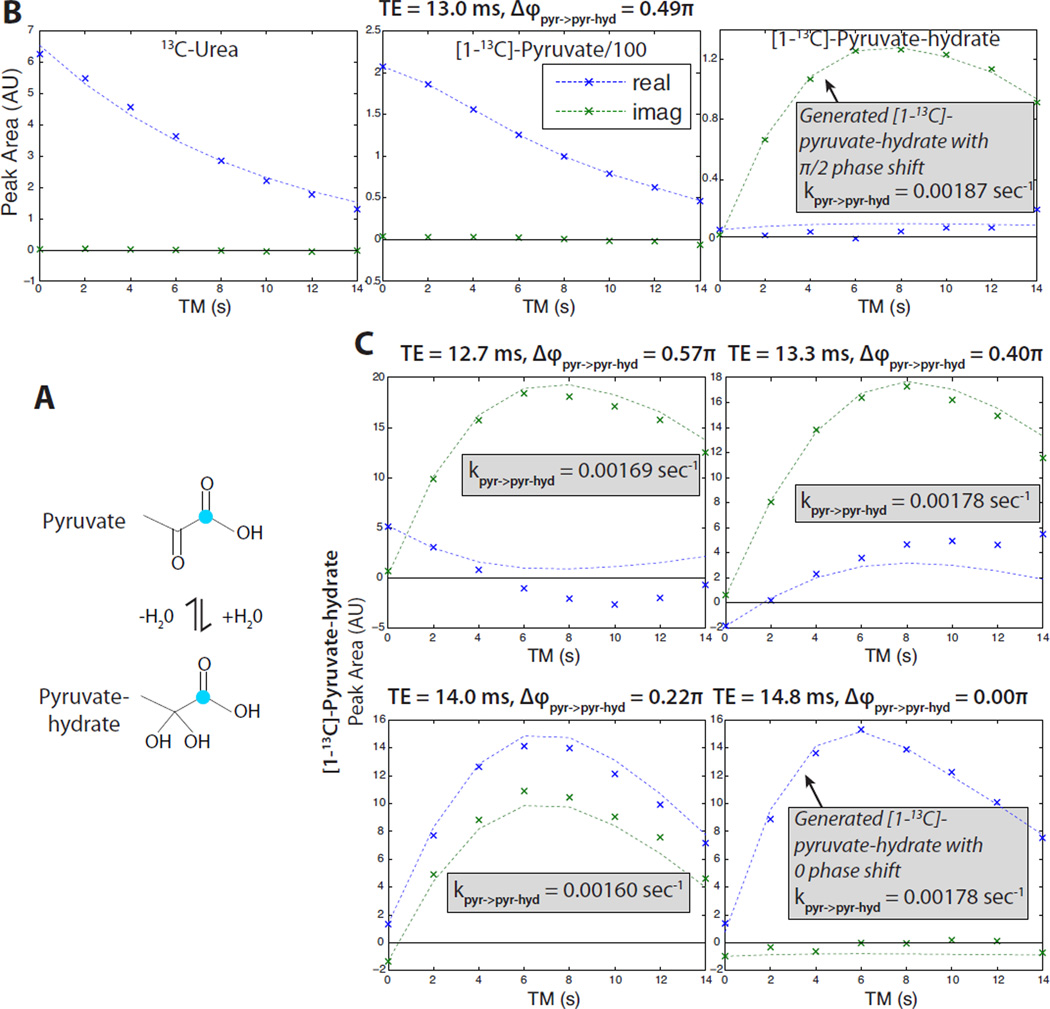
Figure 4.
Validation of the MAD-STEAM method observing pyruvate (pyr) hydration following pre-saturation of the pyruvate-hydrate (pyr-hyd) resonance. (A) Pyruvic acid dissolved into an aqueous solution creates exchange between pyruvate and pyruvate-hydrate, which are in equilibrium. (Teal indicates enriched 13C.) (B) TE = 13.0 ms experiment showing urea (phase reference) and the conversion from pyruvate to pyruvate-hydrate. (C) Various TE experiments showing the phase of the generated pyruvate-hydrate. In all of different TE experiments shown, the experimental data (x’s) phase matches well with the expected curves (dashed lines), which are based on the predicted phase shift, Δϕ, and the fitted conversion rate. Diffferences between the data and expected curves are likely due to imperfect pyruvate-hydrate saturation.