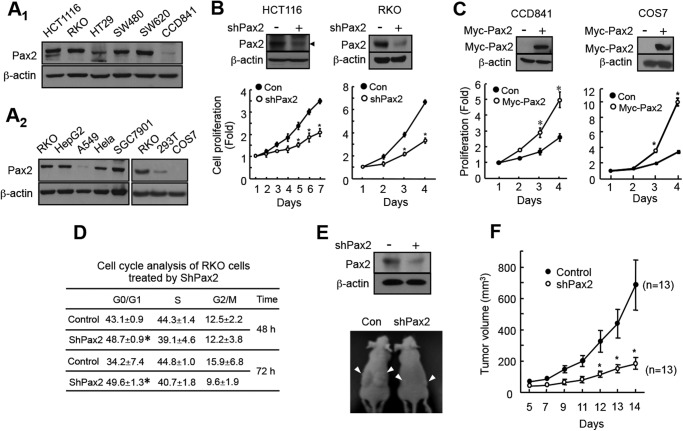
FIGURE 1.
PAX2 promotes proliferation of colon cancer cells. A, expression of PAX2 in colon cancer cells and normal colon epithelial cells (A1) and in other types of cells (A2). Expression of PAX2 was determined by Western blot as described under “Materials and Methods.” B, knockdown of PAX2 inhibited proliferation of colon cancer cells. HCT116 and RKO cells were infected with control (Con) or shPAX2 adenovirus. Cell proliferation was determined as described under “Materials and Methods.” The data are the mean ± S.E. (n = 3). *, p < 0.05 versus control. C, overexpression PAX2 increased cell proliferation. To determine the effect of PAX2 on proliferation of COS7 cell, a pool of COS7 cells that stably expressed PAX2 was prepared as described under “Materials and Methods.” CCD841 cells were transfected with the vector expressing Myc-tagged PAX2. *, p < 0.05 versus control (n = 3). D, knockdown of PAX2 led to cell G1 arrest. RKO cells were infected with control or shPAX2 adenovirus. The infected cells were subjected for cell cycle analysis as described under “Materials and Methods.” *, p < 0.05 versus control (n = 3). E, knockdown of PAX2 inhibited tumor growth of RKO cells. RKO cells were infected with control or shPAX2 adenovirus. 3 × 106 of the infected cells were injected subcutaneously into the flank of nude mice. The upper panel shows the knockdown efficiency of PAX2. The lower panel shows representative mice. F, the volume of the tumors. The tumor volumes were measured 5 days after injection. The data are mean ± S.E. (n = 13). *, p < 0.05 versus control.