FIGURE 5.
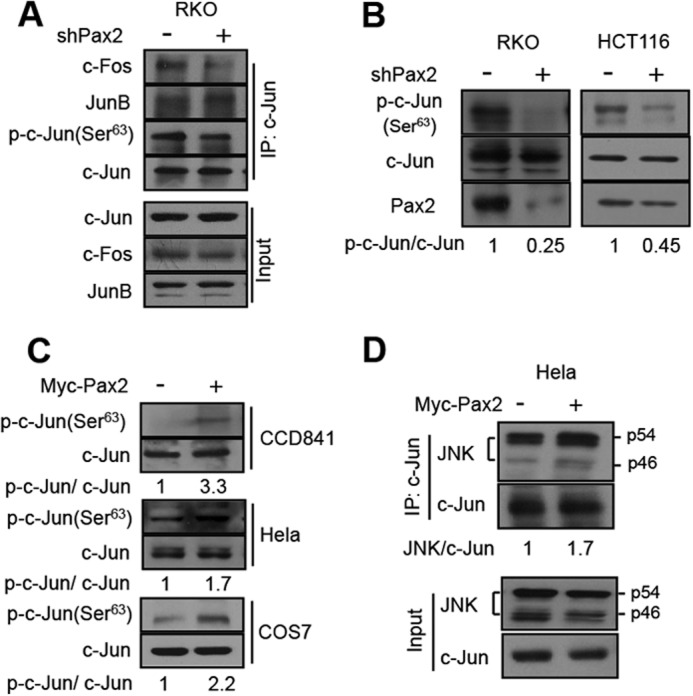
PAX2 enhances phosphorylation of c-Jun. A, knockdown of PAX2 decreased the c-Jun-c-Fos interaction and c-Jun phosphorylation. RKO cells were infected with control or shPAX2 virus. In 48 h, the cells were harvested, and cell lysates were prepared for immunoprecipitation (IP) and immunoblotting. B, knockdown of PAX2 suppressed the phosphorylation of c-Jun. HCT116 and RKO cells were infected with control or shPAX2 adenovirus. In 48 h, the cells were harvested for immunoblotting. The antibody against phospho-c-Jun at Ser-63 was used. The p-c-Jun(Ser-63) to c-Jun ratio (p-c-Jun/c-Jun) was determined by measuring the density of the p-c-Jun(Ser-63) band and normalized to that of c-Jun. C, overexpression of PAX2 increased phosphorylation of c-Jun. CCD841, HeLa, and COS7 cells were transfected with Myc-PAX2 plasmid. The lysates of these cells were used to determine the level of p-c-Jun(Ser-63) by Western blot. p-c-Jun/c-Jun ratio was determined as described above. D, PAX2 enhanced the interaction of JNK and c-Jun. HeLa cells were transfected with control or Myc-PAX2 plasmid. In 24 h, the cells were harvested for determination of the interaction of JNK and c-Jun by means of immunoprecipitation.
