FIGURE 7.
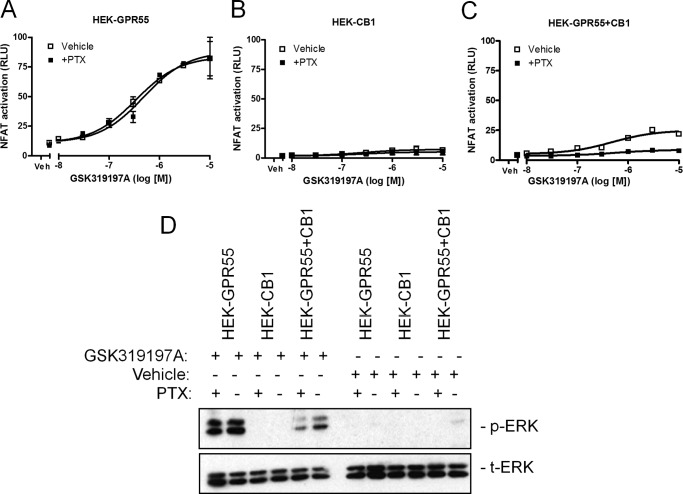
CB1R-mediated Gαi activation is not responsible for the loss of GPR55 signal in HEK-GPR55+CB1 cells. HEK-GPR55 (A), HEK-CB1 (B), or HEK-GPR55+CB1 (C) cells were transfected with the NFAT transcription factor plasmid. 24 h post-transfection cells were preincubated for 4 h with either vehicle (□) or 100 ng/ml of PTX (■) and stimulated with increasing concentrations of GSK319197A. NFAT activation was not altered by PTX in HEK-GPR55 cells (A). No NFAT activation was measured in HEK-CB1 cells after stimulation with the GPR55 agonist GSK319197A (B). In HEK-GPR55+CB1 cells (C), NFAT signaling was impaired in PTX-treated cells (■) when compared with cells treated with vehicle (□). For ERK1/2 phosphorylation (D) determination in the presence or absence of PTX, HEK-GPR55, HEK-CB1, and HEK-GPR55+CB1 cells were serum starved overnight, preincubated with vehicle or 100 ng/ml of PTX for 4 h, and stimulated with vehicle or 2.5 μm GSK319197A for 25 min. ERK1/2 phosphorylation was not altered by PTX in HEK-GPR55 cells. No ERK1/2 activity was observed after vehicle treatment in all cell lines and stimulation with the GPR55 agonist GSK319197A in HEK-CB1 cells. HEK-GPR55+CB1 cells were preincubated with PTX showed decreased pERK1/2 when compared with vehicle preincubated double expressing cell line. Reporter gene assay data are mean ± S.E. from one of three independent experiments performed in duplicates. Data were normalized and expressed as percent of maximum activation, which was set as 100% (A–C). Representative ERK1/2 blot from three independent experiments is shown.