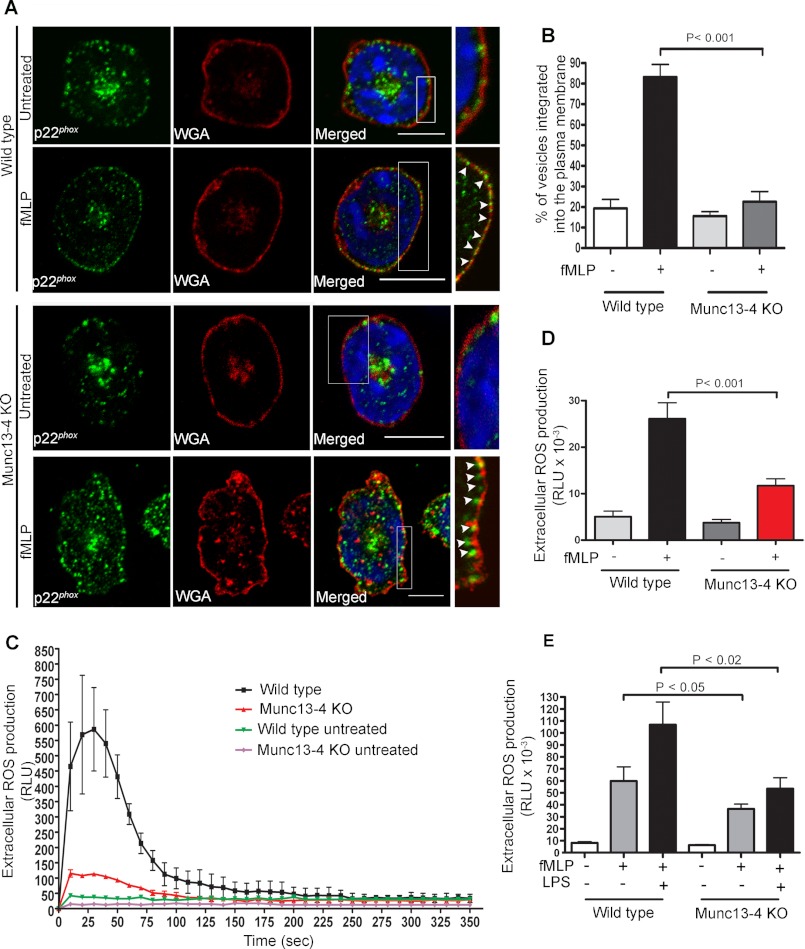
FIGURE 2.
MUNC13-4 KO neutrophils are characterized by an impaired integration of p22phox into the plasma membrane and defective extracellular ROS production. A, confocal microscopy analysis of the distribution of endogenous p22phox in relationship to the plasma membrane. Wild type and MUNC13-4 KO neutrophils were left untreated or stimulated with 10 μm fMLP and fixed, and immunofluorescence analysis was performed using a polyclonal antibody specific for the detection of endogenous p22phox and rhodamine-WGA to label the plasma membrane. The samples were analyzed by confocal microscopy, and representative z-sections for each condition are shown. Inset, the arrowheads point to p22phox-positive granules, which are integrated into the plasma membrane in wild type cells but not in MUNC13-4 KO cells (scale bars, 10 μm). B, quantitative analysis showing the percentage of the p22phox-containing vesicles in the exocytic active zone that are integrated into the plasma membrane. The results are representative of three independent experiments with similar results (mean ± S.E. (error bars)). C, ROS production was measured using bone marrow-derived neutrophils from MUNC13-4 KO and WT mice treated with the cell-impermeant probe isoluminol in the presence of horseradish peroxidase and stimulated with 10 μm fMLP. The representative graph shows the kinetics of extracellular ROS production, which is defective in MUNC13-4 KO cells (red line and symbols). D and E, quantitative determination of the total ROS produced during the time of analysis (calculated as the integral or area under the curve). Results are expressed as mean ± S.E. (error bars); statistical analysis was performed using a non-parametric Mann-Whitney test (D, n = 8; E, n = 3). RLU, relative light units.