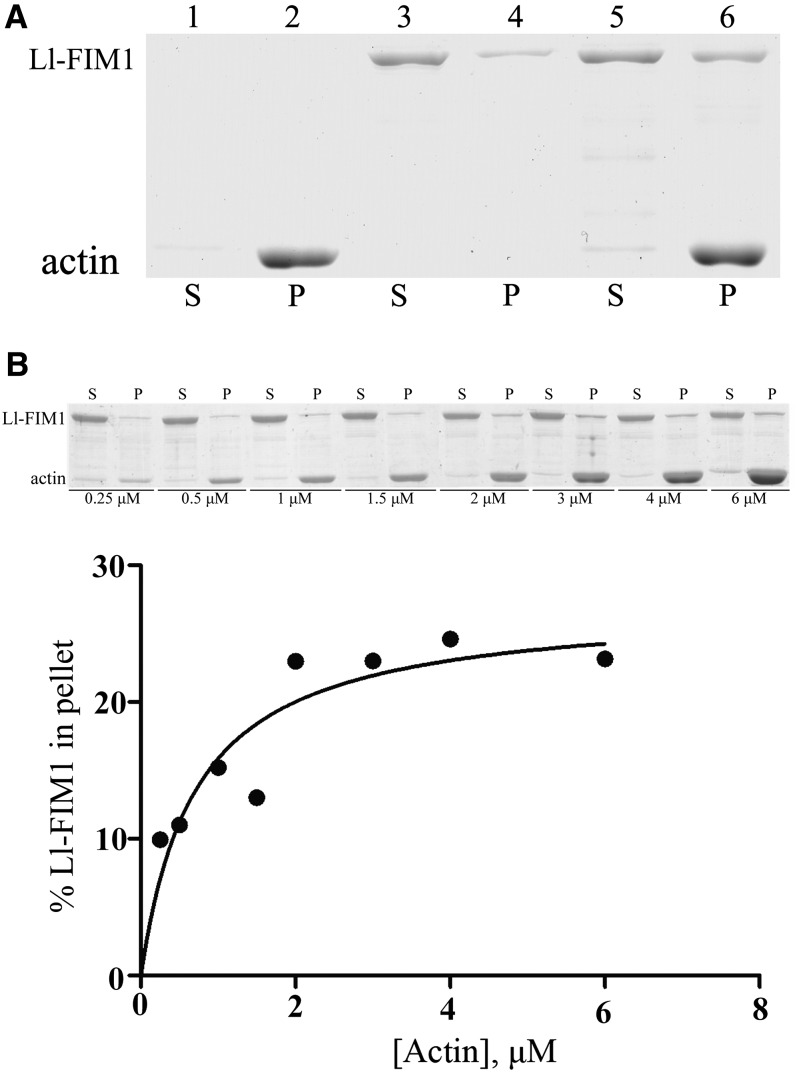
Figure 8.
Ll-FIM1 Can Bind Actin Filaments Directly.
(A) A high-speed cosedimentation assay was used to determine Ll-FIM1 binding to F-actin. A mixture of 3 μM F-actin and 1 μM Ll-FIM1 was centrifuged at 200,000g. The resulting supernatants (S) and pellets (P) were subjected to SDS-PAGE and Coomassie stained. Samples are as follows: lane 1, actin alone supernatant; lane 2, actin alone pellet; lane 3, Ll-FIM1 alone supernatant; lane 4, Ll-FIM1 alone pellet; lane 5, actin plus Ll-FIM1 supernatant; lane 6, actin plus Ll-FIM1 pellet.
(B) Increasing concentrations of phalloidin-stabilized F-actin were mixed with 0.8 μM Ll-FIM1. The concentration of bound Ll-FIM1 was plotted against the concentration of actin and fitted with a hyperbolic curve. For this representative experiment, the calculated dissociation constant (Kd) was 0.73 μM.