Figure 4.
ARC1 Deletion Region in the A. thaliana Genome.
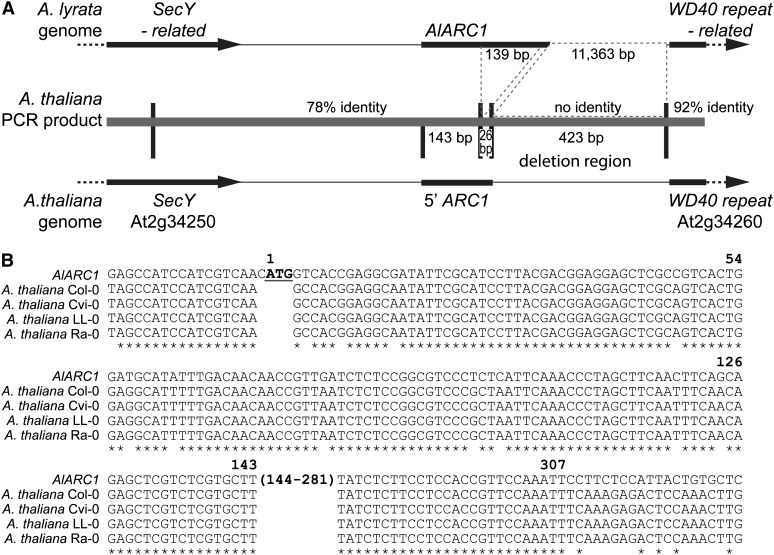
(A) Schematic of the ARC1 region in A. lyrata and A. thaliana. The A. lyrata genome contains an intact ARC1 gene and when compared with A. thaliana shares sequences identity until the deletion break point in the A. thaliana ARC1 pseudogene. The At2g34250 3′ untranslated region and the ARC1 5′ untranslated region/start of the coding region are 78% identical at the DNA sequence level. This is followed by a 139-bp deletion in A. thaliana ARC1 and a small 26-bp sequence of ARC1 that is 100% identical between the two species genomes. The next 423 bp from A. thaliana has no sequence identity to the 11,363-bp region from A. lyrata. The sequence identity returns at 9 bp before the start of At2g34260, and the region is 92% similar up until the end of the sequencing read. The sequence identities were determined using the A. lyrata genome sequence and the sequenced PCR products from 10 different A. thaliana ecotypes.
(B) Sequence alignment of A. lyrata ARC1 to the corresponding region in A. thaliana. PCR products covering this region (shown in [A]) were sequenced for 10 ecotypes (Br-0, Bur-0, C24, Col-0, Cvi-0, Kro-0, Ler-0, LL-0, Mrk-0, Ra-0, and Wei-1). The 10 ecotypes shared identical sequences for the ARC1 5′ coding region and the deletion breakpoint, and sequences from four of these ecotypes are shown aligned to Al-ARC1. The start codon for Al-ARC1 is marked in bold and underlined and is absent in corresponding A. thaliana sequences.