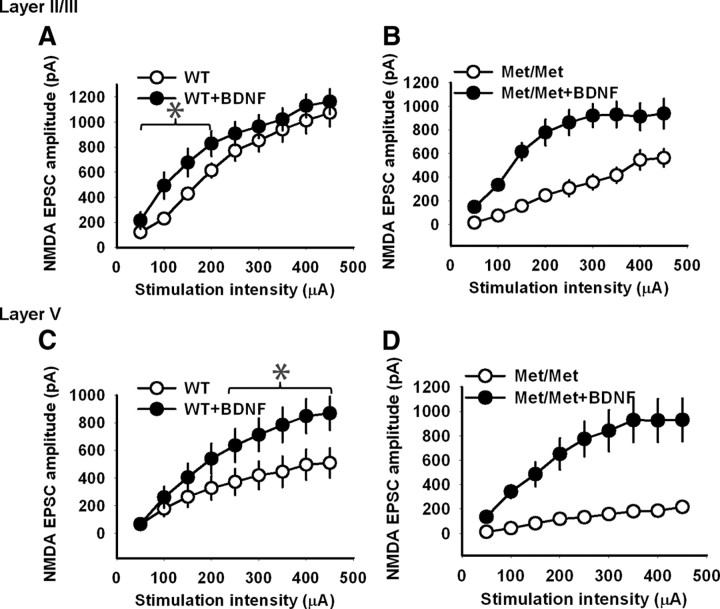
Figure 7.
BDNF enhances NMDA receptor transmission in the IL-mPFC pyramidal neurons of both wild-type and BDNFMet/Met mice. A, NMDA receptor transmission in the layer II/III pyramidal neurons from BDNF-treated (n = 7) and untreated (n = 9) wild-type brain slices. BDNF-treated wild-type slices showed significantly higher NMDA receptor transmission compared with the untreated wild-type slices at stimulation strength 100, 150, and 200 μA (p < 0.05). B, NMDA receptor transmission in the layer II/III pyramidal neurons from BDNF-treated (n = 9) and untreated (n = 10) BDNFMet/Met brain slices. BDNF-treated BDNFMet/Met slices showed significantly higher NMDA receptor transmission compared with the untreated BDNFMet/Met slices (F(1,17) = 21.3, p < 0.001). C, NMDA receptor transmission in the layer V pyramidal neurons from BDNF-treated (n = 7) and untreated (n = 9) wild-type brain slices. BDNF-treated wild-type slices showed significantly higher NMDA receptor transmission compared with the untreated wild-type slices above the stimulation strength of 250 μA (p < 0.01). D, NMDA receptor transmission in the layer V pyramidal neurons from BDNF-treated (n = 8) and untreated (n = 9) BDNFMet/Met brain slices. BDNF-treated BDNFMet/Met slices showed significantly higher NMDA receptor transmission compared with the untreated BDNFMet/Met slices (F(1,15) = 21, p < 0.001). Asterisks denote statistical significance.