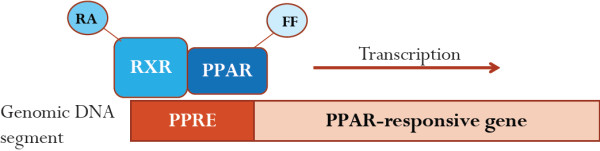
Figure 1.
Agonist-bound PPARs induce gene expression. Activated PPARs must first associate with their co-receptor, retinoid X receptor (RXR), in order to modulate transcription of specific genes. RXR binds to its ligand, retinoic acid, and interacts with PPAR bound to an agonist (e.g. fibrates). Together, RXR and PPAR can then bind to a consensus sequence of nucleotides, known as the PPAR response element (PPRE). PPAR and RXR binding triggers expression of a responsive gene . Abbreviations: RA, retinoic acid, FF, fenofibrate.