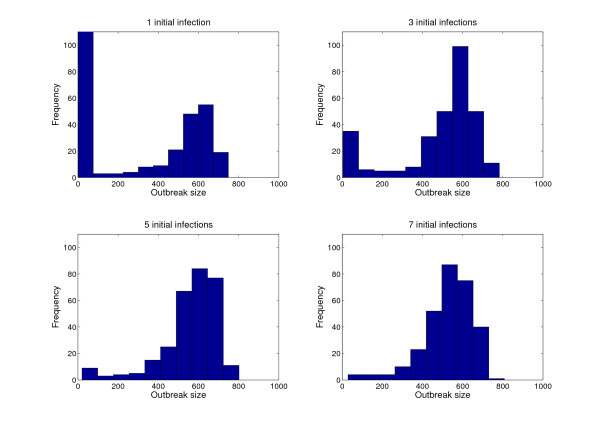
Figure 3.
Effect of the initial number of infectious individuals. The classic stochastic SEIR (susceptible, exposed, infectious, recovered) model tailored to the epidemiology of influenza, based on a latent period of 1.5 days, an infectious period of 3 days, and fixed probability of transmission per contact, was simulated on small-world contact networks based on the Watts and Strogatz network model [74] with an average degree of 4 and disorder parameter (p) of 0.1 in a populations of 1,000 individuals. Initially infectious individuals were selected uniformly at random from the population. Histograms show how the distribution of outbreak sizes shifts to larger epidemics as the initial number of infectious individuals increases.