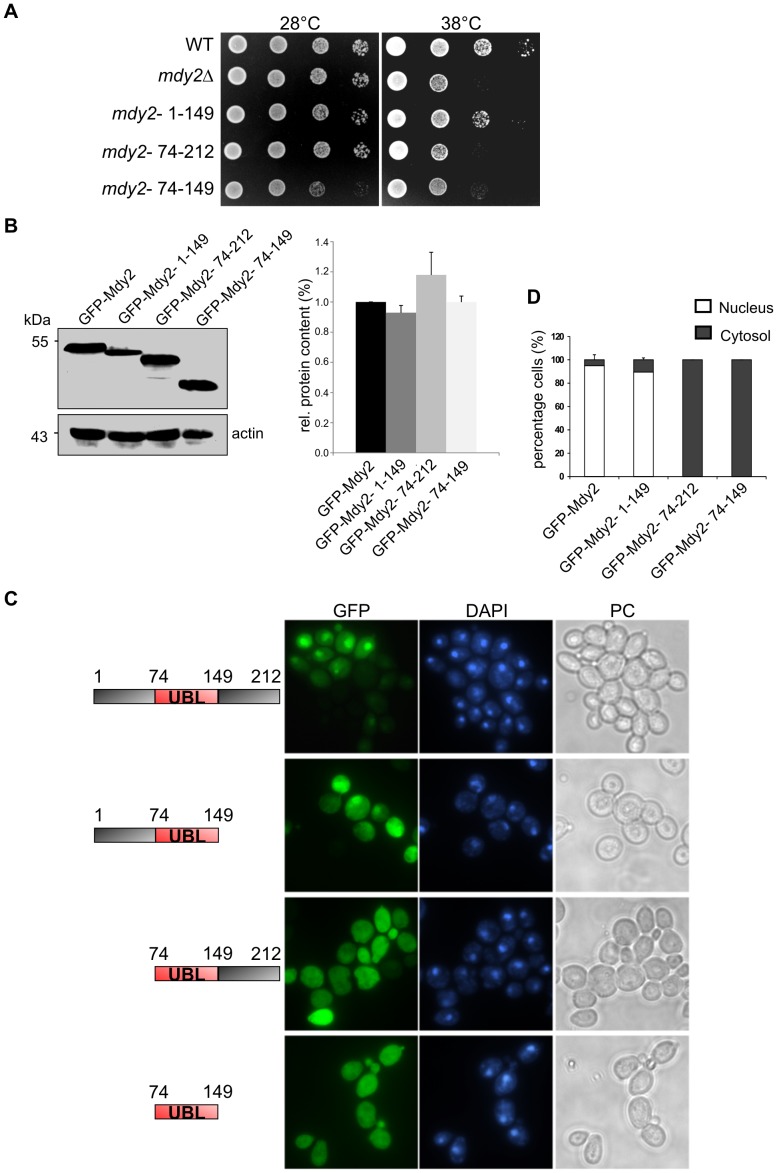
Figure 2. Deletion of the N-terminal region Mdy2 affects GFP-Mdy2 nuclear localization and heat sensitivity.
(A) Mdy2 and different C-, N-, and NC-terminal deletion fragments of Mdy2 open reading frame (see schematics) fused to the C-terminus of GFP protein expressed under the control of GAL1 promoter in mdy2Δ (HZH686) cells. Temperature sensitivity recorded as indicated in Figure 1A. Representative experiments are shown. (B) Protein expression level of GFP-Mdy2 variants shows no difference in mutant cells. The left panel shows Western blot of total protein extracts from GFP-Mdy2, GFP-Mdy2- 1–149, GFP-Mdy2- 74–212, and GFP-Mdy2- 74–149 expressing yeast cells. GFP-Mdy2 was detected using anti-GFP antibody. Protein expression of actin as internal standard was performed using anti-actin antibody, clone C4/MAB1501 (left panel). Quantitative densitometry of protein expression showed no changes in the protein levels of GFP-Mdy2 variants. GFP-Mdy2 was set to 1 (right panel). (C) Visualization of exponentially growing indicated yeast cells was performed using fluorescence microscopy as in Figure 1B. (D) Quantitative and statistical analysis of the subcellular localization of GFP-Mdy2 variants. About 100 cells from three independent experiments were counted. The graphs show the percentage of cells demonstrating nuclear or cytosolic GFP-Mdy2 variant protein distribution.