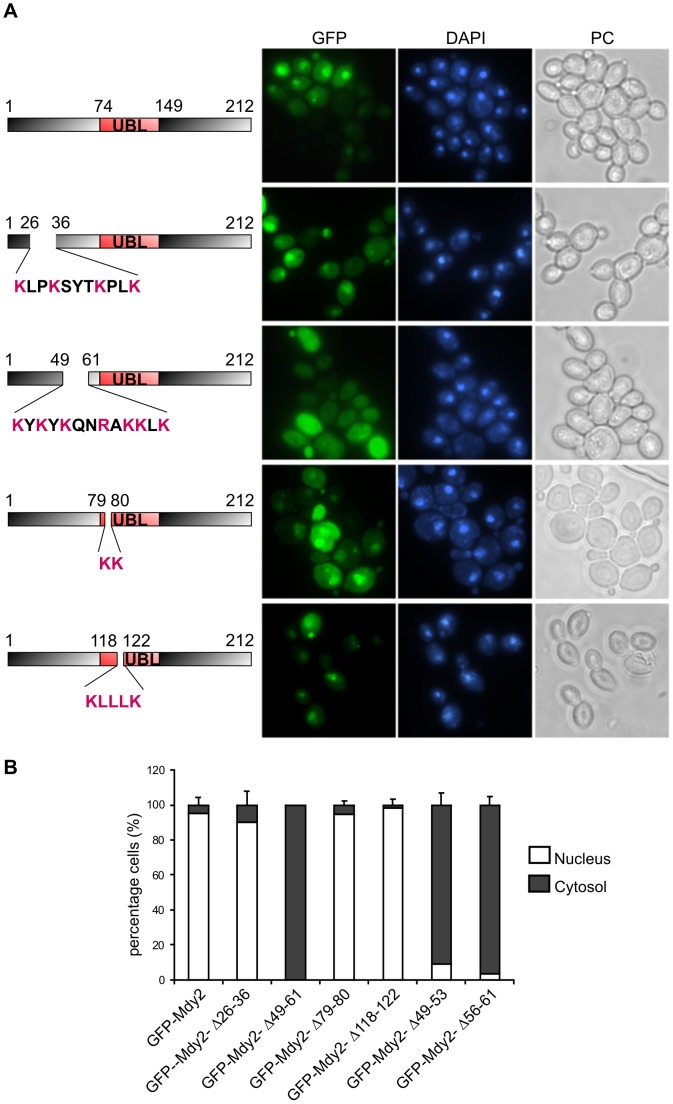
Figure 3. Identification of a nuclear localization signal (NLS) in the N-terminal domain and a nuclear export signal (NES) in the UBL domain of Mdy2.
(A) Green fluorescence images and nuclear DNA of exponentially growing mdy2Δ cells carrying wild type Mdy2 (MDY2) and different putative NLS deletion constructs of Mdy2 (mdy2-Δ26–36, mdy2-Δ49–61, and mdy2-Δ79–80, respectively) were recorded as in Figure 1C. The NLS sequence of Mdy2 is localized between the amino acids 49 and 61 (panel 3). A putative NES deletion construct of Mdy2 (see schematic) was fused to the C-terminus of GFP protein, expressed under the control of GAL1 promoter in mdy2Δ (HZH686) cells, and analyzed as in Figure 1B. The NES sequence of Mdy2 is localized between amino acids 118 and 122 (panel 5). (B) Quantitative and statistical analysis of the subcellular localization of Mdy2 mutants with defective nuclear localization, Mdy2-ΔNLS, and nuclear export, Mdy2-ΔNES as in Figure 2D.