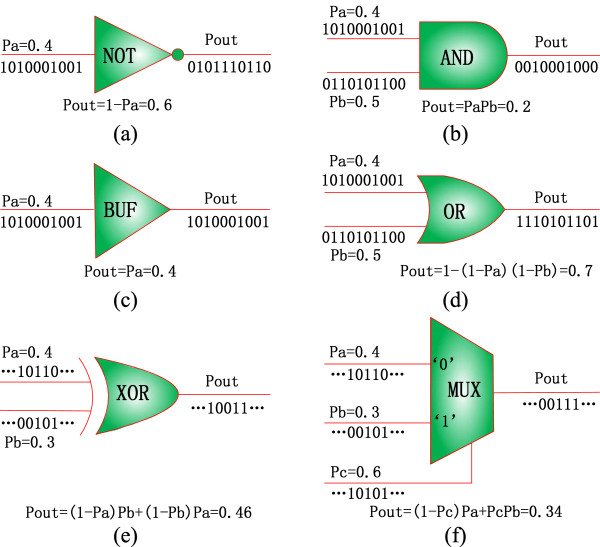
Figure 1.
Stochastic logic. (a) a NOT gate, (b) an AND gate, (c) a buffer, (d) an OR gate, (e) an XOR gate and (f) a multiplexer. Stochastic logic performs arithmetic operations on the input probabilities encoded in the random binary bit streams. A probability is represented by a proportional number of bits, i.e., the mean number of 1’s in a binary sequence. For illustration, a sequence length of 10 bits is used from (a) to (d); however longer sequences are typically needed in a practical application, as shown in (e) and (f).