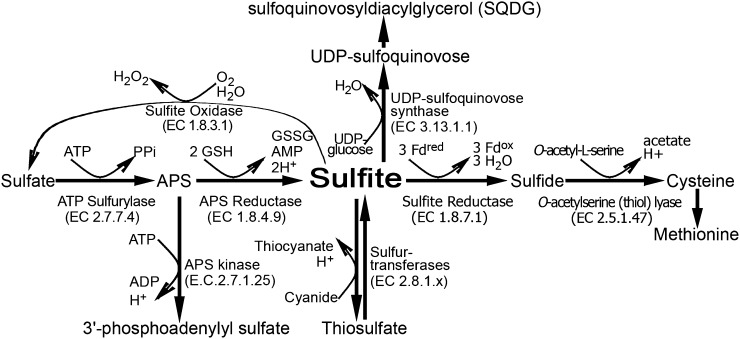
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of sulfite network enzymes in plants. Sulfite is generated from sulfate in two consecutive steps. In the first step, ATP sufurylase catalyzes the adenylation of sulfate to APS, and then sulfite is produced in the chloroplast by the glutathione-dependent APR. In the chloroplast, the generated sulfite can be further reduced to sulfide by the ferredoxin-dependent SiR. The sulfide together with O-acetyl-l-Ser are the substrates for Cys biosynthesis catalyzed by OAS-TL. Alternatively, the chloroplast-localized sulfite can enter the sulfolipid reductive pathway to generate SQDG in two consecutive steps. In the first step, UDP-sulfoquinovase is catalyzed by SQD1, employing sulfite and UDP-Glc as substrates, while in the second step, SQDG is catalyzed by SQDG synthase, employing UDP-sulfoquinovose and diacylglycerols as substrates. Sulfite localized to the cytosol and mitochondria may be detoxified to thiosulfate by the STs or be generated by these enzymes from thiosulfate and cyanide (Nakamura et al., 2000; Papenbrock and Schmidt, 2000a; Tsakraklides et al., 2002). Sulfite can be oxidized to sulfate by the molybdenum cofactor-containing enzyme, peroxisomal SO. Fdox, Oxidized ferredoxin; Fdred, reduced ferredoxin; GSSG, oxidized glutathione; H2O2, hydrogen peroxide; PPi, diphosphate.