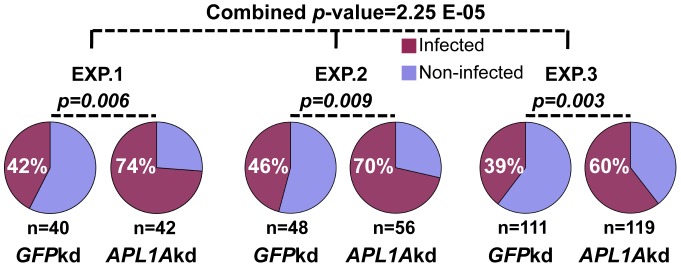
Figure 4. APL1A silencing renders mosquitoes significantly more susceptible to P. falciparum infection.
Silencing of APL1A in A. gambiae Ngousso results in significantly higher infection prevalence in mosquitoes fed on in vitro cultured P. falciparum gametocytes. For each experiment (EXP.), a Chi-square analysis was performed to compare infection prevalence between GFP-knockdown (GFPkd) and APL1Akd. A meta-analysis using the Fisher method [33] was also used to combine the p-values of the three independent experiments.