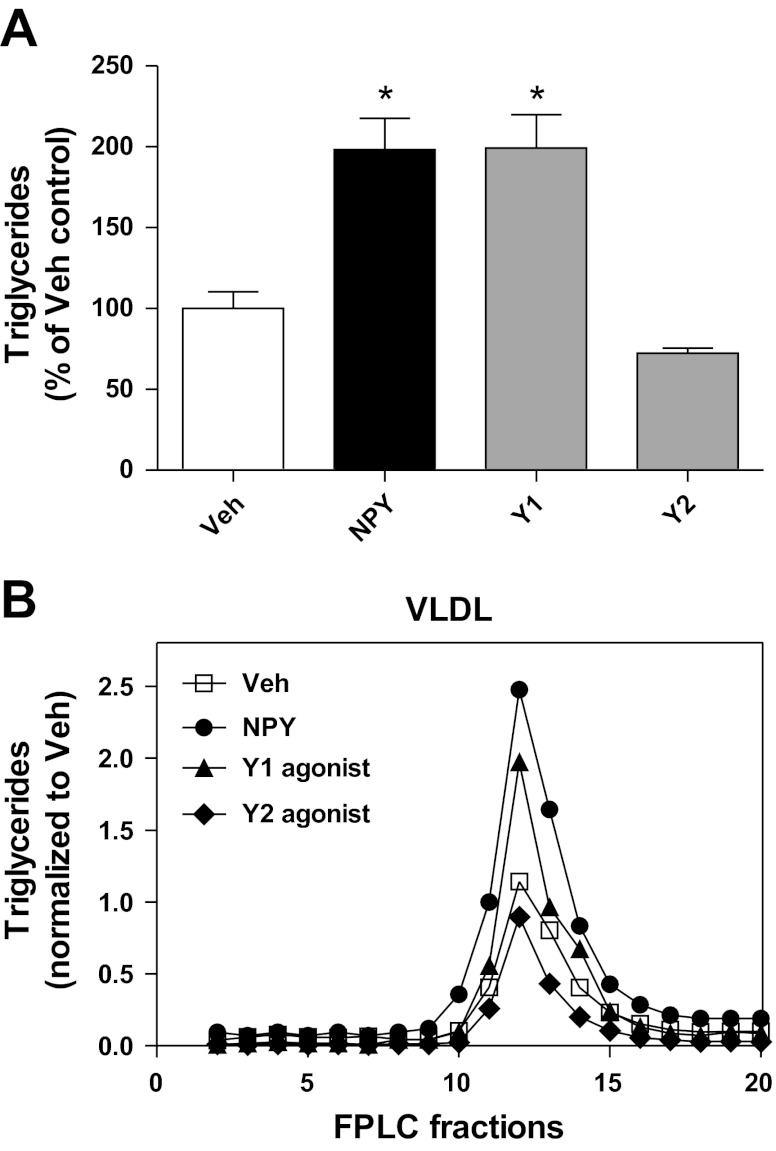
Fig. 4.
Effects of CNS NPY receptor subtypes Y1 and Y2 on hepatic VLDL-TG secretion. A and B: NPY (1 nmol), Veh, or receptor agonists for either Y1 ([F7, P34]-NPY, 1 nmol) or Y2 [human peptide YY-(3–36), 1 nmol] were given icv in the absence of tyloxapol to 4-h-fasted lean rats (n = 6–13/group), and trunk blood was collected at 120 min postinjection. Each receptor subtype agonist was tested in a separate cohort of animals, and each cohort was matched to its own Veh control group, so plasma TG levels of each treatment group were normalized to their matched Veh controls. A: plasma TG levels of each treatment group (%Veh control) are shown. Data are means ± SE. *Statistical significance (P < 0.05), as determined by 1-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's posttest analysis, for all comparisons relative to Veh. B: the TG content of FPLC fractions after size fractionation of pooled plasma samples is illustrated. Column fractions 10–20, with the size range corresponding to VLDL, are illustrated to allow comparisons between the different icv treatment groups: Veh (□), NPY (●), Y1 receptor agonist (▲), and Y2 receptor agonist (◆).