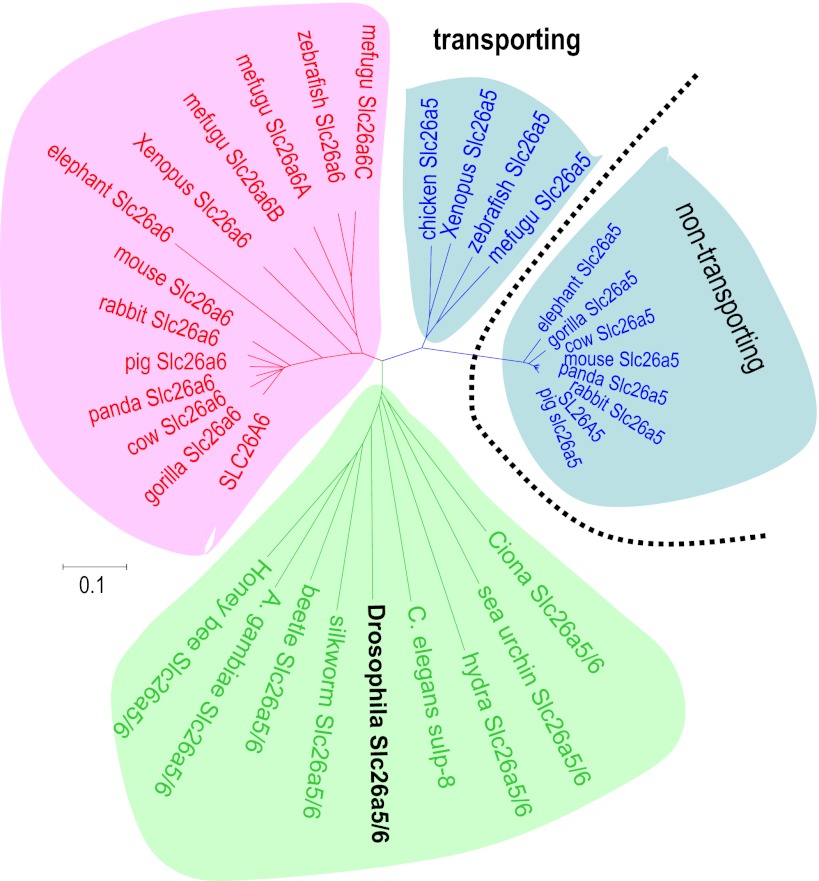
Fig. 6.
Phylogenetic tree of animal Slc26a5 and Slc26a6 proteins. Phylogeny of Slc26a5 and Slc26a6 from several species [human (Homo sapiens), pig (Sus scrofa), giant panda (Ailuropoda melanoleuca), rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus), cow (Bos taurus), mouse (Mus musculus), gorilla (Gorilla gorilla), elephant (Loxodonta africana), chicken (Gallus gallus), Xenopus (X. tropicalis), zebrafish (D. rerio), mefugu (T. rubripes), sea squirt (Ciona intestinalis), fruit fly (Drosophilia melanogaster), silkworm (Bombyx mori), beetle (Tribolium castaneum), mosquito (Anopheles gambiae), honey bee (Apis mellifera), and roundworm (C. elegans)]. The sequences used are as follows with the accession numbers in parentheses: human SLC26A5 (AF523354); human SLC26A6 (NM_134263); chicken Slc26a5 (NP_001072945); Xenopus Slc26a5; Xenopus Slc26a6; Slc26a5 (NM_201473); zebrafish Slc26a6 (BC155340); Ciona (C. intestinalis) Slc26a5/6 (AAP57206); fly (D. melanogaster) Slc26a5/6 (NM_140767); honey bee (Apis mellifera) Slc26a5/6 (XM_001121249); and C. elegans sulp-8 (NM_073092). Bars indicate 10% replacement per site.