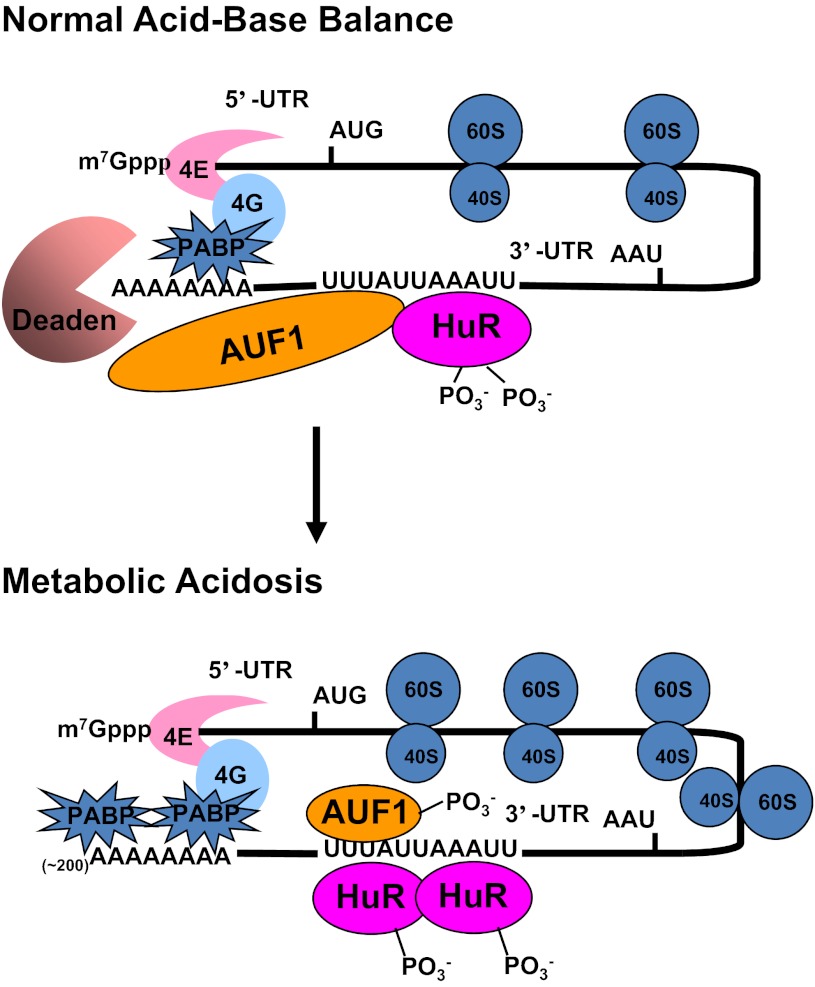
Fig. 9.
Current model for the pH-responsive stabilization of PEPCK mRNA. Interactions between the cap binding proteins (4E and 4G) and the polyA binding protein (PABP) cause a mRNA to form a circular structure that enhances translation. During normal acid-base balance, both HuR and AUF1 bind to the AU-rich sequences within the 3′-UTR of the PEPCK mRNA that function as a pH response element. The resulting complex recruits a deadenylase (Deaden) that removes the polyA tail and causes dissociation of the PABPs. The deadenylated mRNA is rapidly degraded from the either the 3′-end by the exosome or the 5′-end by decapping and degradation in processing bodies. In response to metabolic acidosis, the levels of phosphorylation of HuR and AUF1 are decreased and increased, respectively. These changes lead to increased binding of HuR and a remodeling of the HuR/AUF1 complex that is bound to the 3′-UTR of PEPCK mRNA. The new complex is less effective at recruiting the Deaden and thereby promotes stabilization of the PEPCK mRNA.