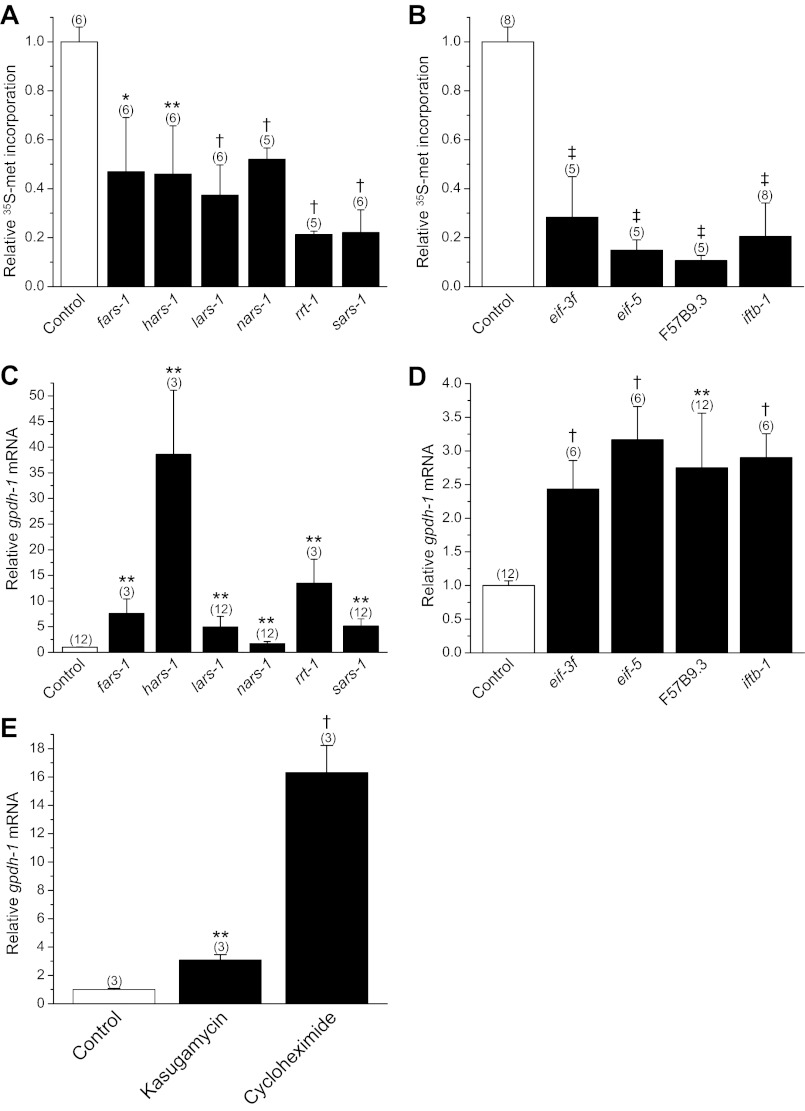
Fig. 1.
Relationship between inhibition of protein synthesis and gpdh-1 expression. A and B: [35S]methionine incorporation into total protein in worms fed bacteria expressing scrambled double-stranded RNA (dsRNA, control) or dsRNA homologous to regulators of gpdh-1 (rgpd) genes encoding aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases (fars-1, hars-1, lars-1, nars-1, rrt-1, and sars-1 encode phenylalanyl-, histidyl-, leucyl-, asparaginyl-, arginyl-, and seryl-tRNA synthetases, respectively) and eukaryotic translation initiation factors (eif-3f, eif-5, F57B9.3, and iftb-1 encode the eIF3 F-subunit, eIF5, eIF4A, and eIF2 β-subunit, respectively). Values are expressed relative to [35S]methionine incorporation in control worms. *P < 0.04, **P < 0.01, †P < 0.001, ‡P < 0.0001, compared with control. C and D: relative gpdh-1 mRNA levels in worms fed dsRNA expressing bacteria. **P < 0.01; †P < 0.001, compared with control. E: effect of inhibition of protein synthesis for 6 h by 1 mg/ml kasugamycin or 1 mg/ml cycloheximide on gpdh-1 mRNA levels. gpdh-1 mRNA is expressed relative to that observed in control worms with no drug treatment. **P < 0.01, †P < 0.001, compared with control. All values are means ± SE; n is shown in parentheses above each data point.