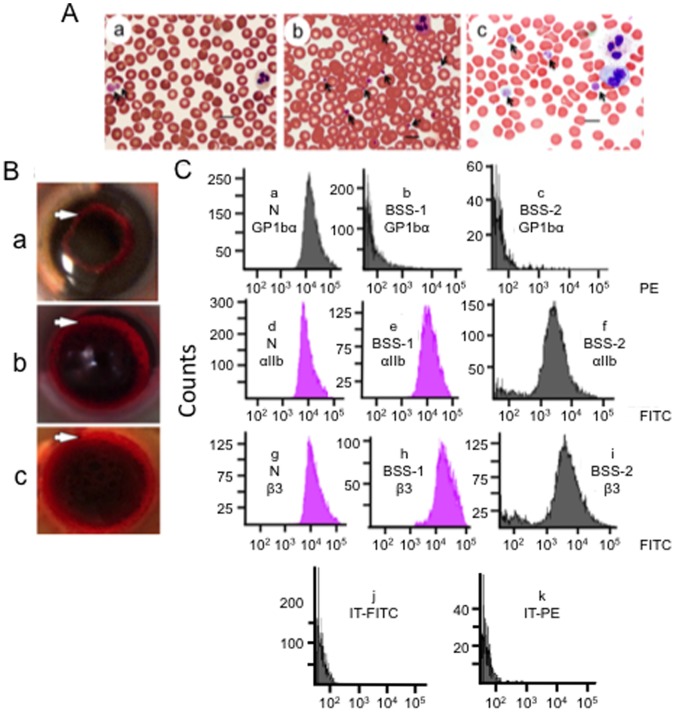
Figure 1. Platelets of BSS patients.
(A) Blood smears were stained with Volu-Sol Dip Stain. (a) BSS-1. The platelets (arrows) vary in size and exhibit a granular composition with a fuzzy coat. Giant platelets (>5 µm) are indicated by arrows. (b). Normal blood showing platelets (arrows) at 1–3 µm diameter. (c) BSS-2. Giant platelets (>5 µm) are indicated by arrows. The blood smears were viewed with a Nikon E600 Eclipse microscope containing a Plan Apo VC 100×/1.40 N.A. Oil lens, acquired with a Nikon DS Ri1 color digital camera via Nikon Elements AR 3.2 imaging software, and saved as TIFF files. Measurements of cells were obtained with the measurement tool of the Nikon Elements-AR 3.2 imaging software. The bars on all images represent 10 µm. (B) Whole blood clot retraction of (a) BSS-1, (b) normal human, and (c) BSS-2 clots. Similar rings of retraction (white arrows) are observed in normal control and BSS blood after 30 min. (C) Flow cytometric analysis of formaldehyde-fixed platelets of PRP from normal (N) blood and PRP from BSS-1 and BSS-2. Surface expression of platelet GPIbα (CD42b) in a (a) normal control. GPIbα is greatly reduced and similar to the isotype control in (b) BSS-1 and (c) BSS-2 platelets. Surface expression of integrin αIIb (CD41) in a (d) normal control, as well as (e) BSS-1 and (f) BSS-2 platelets. Surface expression of integrin β3(CD41) in αIIb/β3 in a (g) normal control, and (h) BSS-1 and (i) BSS-2 platelets. Normal-to-increased expression of integrin αIIb and the αIIb/β3 complex is observed in BSS platelets. (j, k) Isotype control for (j) FITC and (k) PE with normal platelets; BSS-1, BSS-2, GT-1, GT-2, and GT-3 platelets showed very similar controls.