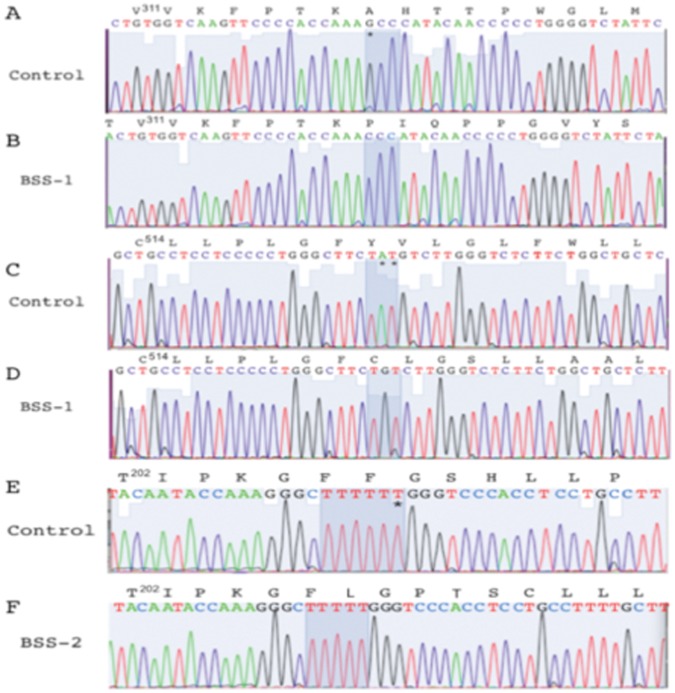
Figure 2. Nucleotide sequence of the mutated regions of GPIBA in BSS patients.
In each case, the sequence data are displayed for one example PCR clone within the GPIBA gene in the genome, along with the readouts of the nucleotides of the translated products. No uncertainties were noted in any clones sequenced in these regions. (A) Normal human GPIBA sequence of the region spanning amino acids V311–M326 of GP1b. (B) The 1st nucleotide (G*) of the codon for A318 is deleted in the paternal allele of BSS-1 (A), thus altering the reading frame of the protein. (C) Normal human GP1b sequence of the region spanning amino acids C514–L529. (D) The 2nd and 3rd nucleotides (A*T*) of the codon for Y521 are deleted in the maternal allele of BSS-1 (C), thus altering the reading frame of the protein. (E) Normal human GP1b sequence of the region spanning amino acids T202–V214. (F) A single T of the group of 6 T residues encoding F207–F208 of GP1b has been deleted (*) in both alleles of BSS-2 (E), altering the reading frame of the protein. The protein sequences are numbered from M1 of the ORF. The corresponding nucleotide sequences are numbered from the 1st residue of the ATG translation initiation sequence.