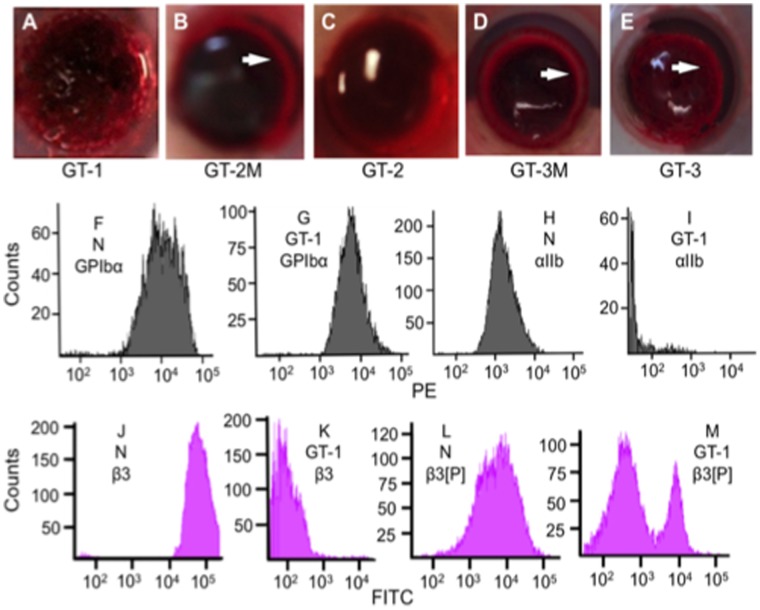
Figure 4. Platelets of GT patients.
Whole blood clot retraction of (A) GT-1, (B) GT-2M, and (C) GT-2, (D) GT-3M, and (E) GT-3 clots. A ring of retraction (white arrows) is observed in GT-2M and GT-3M clots, whereas the GT-1, GT-2, and GT-3 specimens displayed much weaker retraction at 30 min. (F-M) Flow cytometric analysis of normal and GT-1 PRP. (F, G) Surface expression of GP1bα (CD42b) in (F) normal and (G) GT-1 platelets show similar expression levels of GP1bα. (H, I) Surface expression of integrin αIIb (CD41) in (H) normal and (I) GT-1 platelets show reduced expression of CD41 in GT-1 platelets, likely owing to the reduced levels of β3 and thereby reduced amount of surface αIIb/β3 complexes. (J) Surface expression of integrin β3 (CD61) in normal platelets from PRP shows one peak demonstrating the presence of integrin β3 in the αIIb/β3 complex. (K) Surface expression of platelet β3 of αIIb/β3 in GT-1 PRP shows a lack of reactivity of platelets with this antibody. (L) Surface expression of integrin β3[740–769] (β3[P]) in normal PRP. (M). Surface expression of integrin β3[740–769] (β3[P]) in GT-1 PRP. The downfield peak in (M) is similar to isotype controls and likely corresponds to the protein expressed by the truncated allele of integrin β3 in αIIb/β3 in this patient. The smaller peak in (M) to the right shows a reactivity with the full-length allele of integrin β3 in this complex, which harbors the [R131P] mutation but expresses the [740–769] peptide region of the protein.