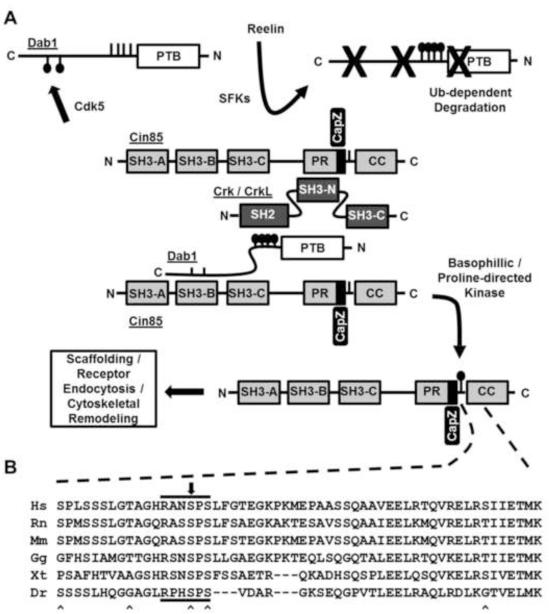
Fig. 5.
(A) Simple model depicting phospho-dependent regulation of the Dab1-Cin85 protein complex. Dab1 phosphorylation by Cdk5 at Ser400 and Ser491disrupts its binding to Cin85. Conversely, phosphorylation of Cin85 at Ser587 disrupts its binding to Dab1. Upon Reelin stimulation Cin85 levels could increase in proximity of the Reelin signaling complex via recruitment to pY-Dab1 through the Crk/CrkL family of adaptors. Ultimately phsphotyrosyl-Dab1 is targeted for proteasome-dependent degradation and Cin85 phosphorylation at Ser587 can accumulate. It is hypothesized that phospho-Ser587 Cin85 regulates its role in receptor endocytosis or actin cytoskeletal remodeling. (B) Multiple sequence alignment shows Ser587 lies in a RXXSPS motif conserved among Cin85 orthologues in common vertebrates. The black arrow above the alignment indicates the position of Ser587. “^” markings below the alignment indicate the positions of previously identified phosphorylation sites. Letters preceding sequences indicate the first letter of both the genus and species of the Cin85 orthologues (human, rat, mouse, chicken, frog, zebrafish).