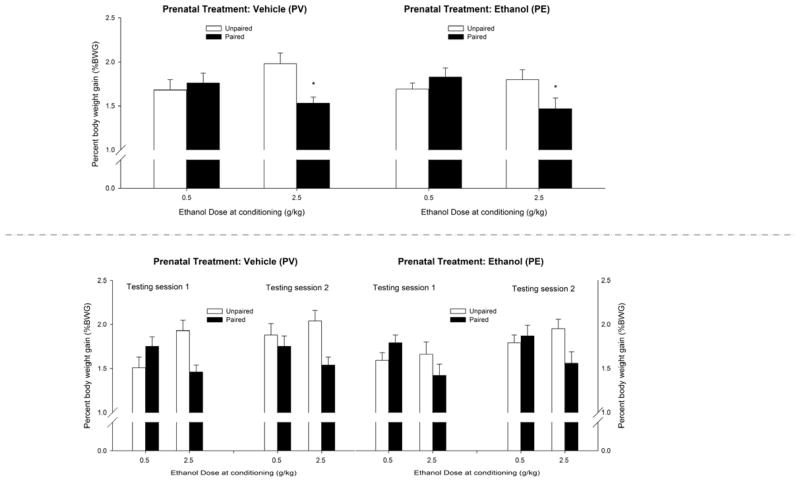
Figure 4.
Ethanol-induced conditioned taste aversion in infant rats derived from pregnant rats that were given 2.0 g/kg ethanol or vehicle (water) intragastrically (PE and PV groups, respectively) on gestational days 17 to 20, with CS (saccharin) intake depicted as percent body weight gain (%BWG) in a 10 min test. Twenty-four hours prior to conditioning, the pups were treated with the KOR antagonist nor-BNI (0.0 or 2.5 mg/kg, i.p.). During conditioning (PD14–15), the pups were exposed to a saccharin solution and intubated with ethanol (0.5 or 2.5 g/kg) immediately following the infusion. Conditioning session 2 on PD15 also served as a test session because the animals were infused with saccharin and assessed for intake prior to receiving the corresponding ethanol dose. A second test session was conducted on PD16. The upper panel depicts the average saccharin acceptance (%BWG) across the test sessions as a function of prenatal treatment and ethanol dose during conditioning. The lower panel depicts these data disaggregated by test session (1 or 2). To facilitate data visualization, the data were collapsed across sex and nor-BNI treatment. The latter factors did not affect avoidance scores or significantly interact with the remaining factors. Asterisks (*) in the upper panel indicate significant differences between a paired group and its corresponding unpaired control (p < 0.05). Vertical bars indicate the SEM.