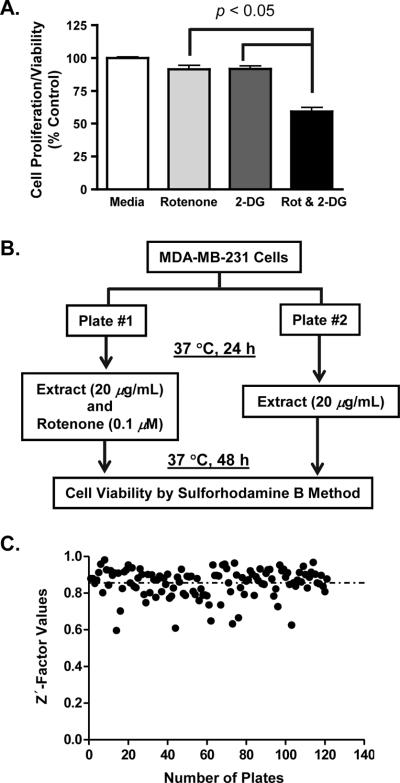
Figure 1.
Development of an MDA-MB-231 cell-based functional assay to identify aerobic glycolysis inhibitors. (A) Effects of rotenone and 2-deoxy-d-glucose (2-DG) on cell proliferation/viability. MDA-MB-231 cells were exposed to 2-DG (3 mM) in the presence or absence of rotenone (0.1 μM) for 48 h. Cell viability was measured by the sulforhodamine B method. Data shown are average + standard deviation from three independent experiments, each performed in duplicate (n = 6). The difference between specified groups is considered statistically significant when p < 0.05. (B) A schematic flow-diagram of the assay system for the discovery of glycolysis inhibitors. (C) Distribution of Z'-factor values between the media control and 2-DG (3 mM) plus rotenone (0.1 μM) from the evaluation of 121 extract sample plates. The dotted line indicates the average Z'-factor value (0.856) from all the plates.