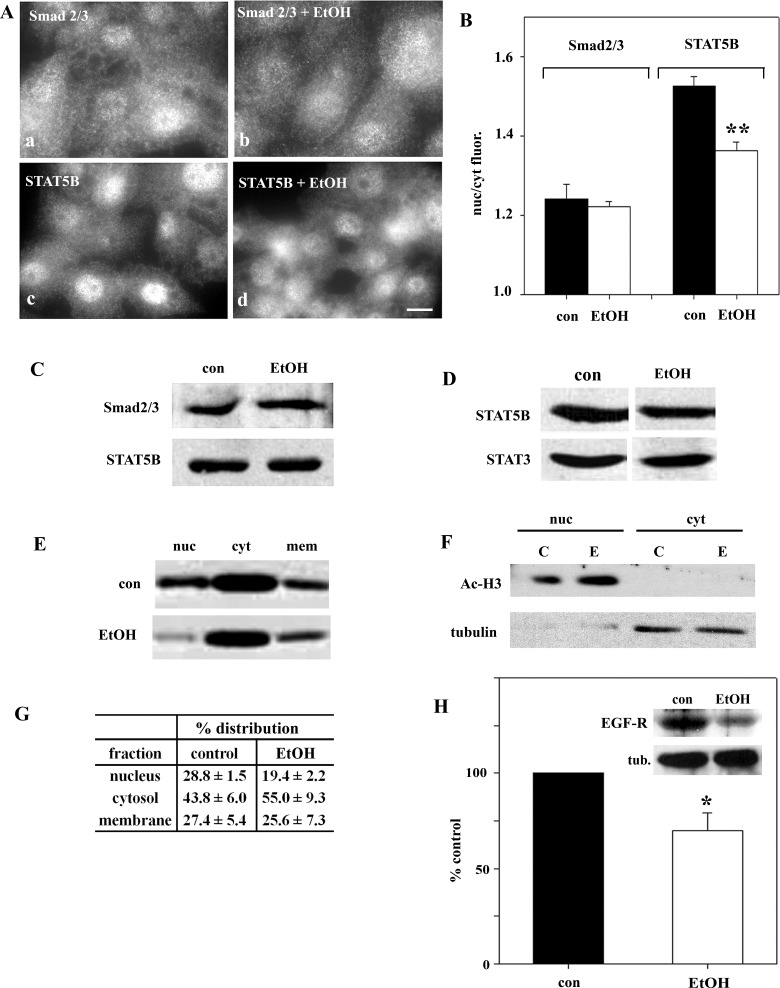
Fig. 5.
Decreased nuclear STAT5B in VL-17A cells and livers from ethanol-fed rats. A: VL-17A cells were incubated in HEPES-buffered medium for 24 h in the absence or presence of 50 mM ethanol. Cells were fixed and immunolabeled for Smad2/3 or STAT5B. ∗, Selected bile canaliculi. Scale bar, 10 μm. B: ratio of nuclear to cytoplasmic fluorescence intensities was calculated for Smad 2/3 and STAT5B. Values are means ± SE from ≥3 independent experiments. **P ≤ 0.01. C: control and ethanol-treated VL-17A cells were immunoblotted for Smad2/3 or STAT5B. D: male Wistar rats were pair-fed control or ethanol Lieber-DeCarli liquid diets for 5 wk. Liver whole homogenates from control and ethanol-fed rats were immunoblotted for STAT5B or STAT3. Blot is representative of 3 independent experiments. E: liver whole homogenates from control and ethanol-fed rats were subfractionated to prepare nuclear (nuc), cytosolic (cyt), and nonnuclear membrane (mem) samples. Fractions were immunoblotted for STAT5B. A representative blot is shown. Immunoreactivity was measured using densitometry and plotted in G. Values are means ± SE from 3 independent pairs of rats. F: to assess fraction purity, cytosolic and nuclear fractions were immunoblotted for acetylated histone H3 (Ac-H3, nuclear marker) or α-tubulin (cytosolic marker). C, control; E, ethanol-fed. H: control and ethanol-treated cells were immunoblotted for EGF receptor (EGF-R) or α-tubulin (tub) as a loading control (inset). Immunoreactivity was measured using densitometry, and EGF-R levels were normalized to tubulin levels and calculated as percentage of control. Values are means ± SE from 4 independent experiments. *P ≤ 0.046.