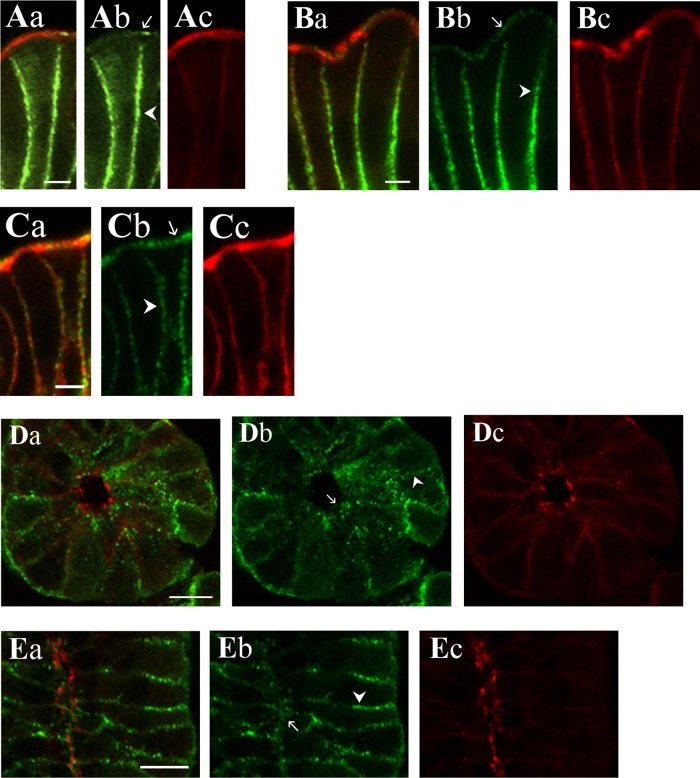
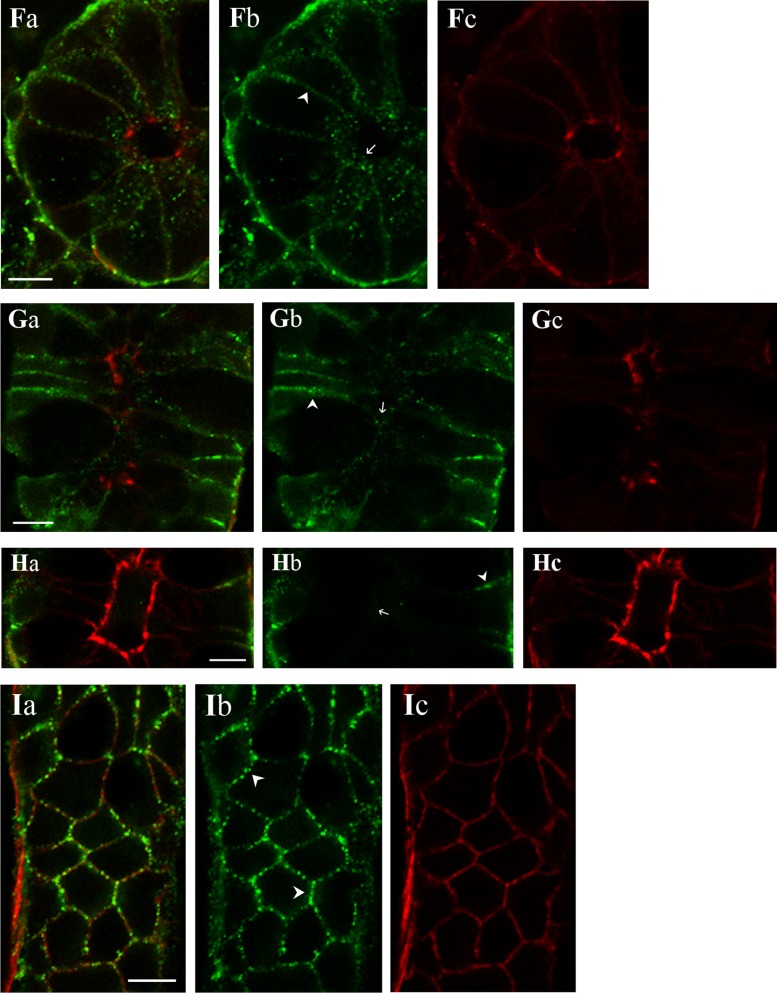
Fig. 9.
KCa1.1α localization in the colonic epithelium. KCa1.1α was detected in distal colonic mucosa by immunoreactivity to 3 antibodies (KCa1.1αIR; green; b). Actin detected with labeled phalloidin revealed the morphology of the epithelium (red; c) for cellular localization of KCa1.1αIR (a). Prominent KCa1.1αIR was apparent in surface cells along the lateral cell margins (arrowhead) and the brush-border membrane (arrow). Labeling was similar with each antibody, anti-KCa1.1α-L6/60 (A), anti-KCa1.1α-H300 (B), and anti-KCa1.1α-QEDRL (C). Scale bars, 5 μm. Crypt cross-section and longitudinal profiles are shown (D–I). Prominent KCa1.1αIR was apparent in crypt cells along the lateral cell margins (arrowhead). Apical poles also exhibited punctate KCa1.1αIR (arrow). Labeling was similar with anti-KCa1.1α-L6/60 (D and E) and anti-KCa1.1α-H300 (F and G) antibodies. Anti-KCa1.1α-QEDRL (H and I) exhibited KCa1.1αIR only along the lateral margins at the basal end of the crypt cells (arrowhead); luminal margin is indicated by an arrow. Scale bars, 10 μm. Use of the secondary antibody alone led to loss of labeling (data not shown), indicating that the primary antibodies were necessary for the labeling observed.