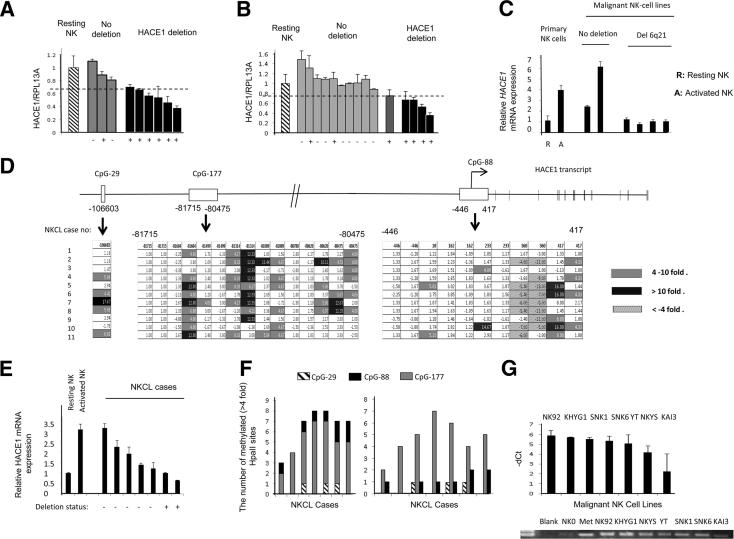
Figure 1.
HACE1 is silenced through a combination of hemizygous deletion and CpG island hypermethylation in NKCL samples. A and B: NK cell lines and NKCL cases with or without deletion were determined by the HACE1/RPL13A ratio for each sample. NKCL cases with HACE1/RPL13A <0.75 that of human resting primary PB NK cell DNA were defined to have deletion. HACE1/RPL13A for each sample represented the average of two independent experiments for both HACE1 and RPL13A. The deletion status of the NKCL cases by aCGH was shown with the ± signs at the bottom of the figure. The plus sign indicates a hemizygous deletion in the minimal common region of 6q21 according to the two previous reports that applied bacterial artificial chromosome-aCGH on NK cell lines and NKCL cases16 or Cartes d’Identité des Tumeurs CGH on NKCL cases.19 The dashed horizontal bar represents the cutoff used to determine the deletion status of the NK cell lines and NKCL cases. C: Quantification of HACE1 mRNA in NK cell lines. The HACE1 mRNA expression in NK cell lines was determined with RT-qPCR. Relative expression values were normalized to the values of the resting NK cells. Resting and 4-day IL-2–activated primary PB NK cells were used as control. Data are means ± SDs of two experiments. D: Hypermethylation of the three CpG islands, CpG-29, CpG-177, and CpG-88, in NKCL cases was determined with MSCC. The differential methylation of the HpaII sites was shown after normalization of the HpaII count sites to the count sites of the 48-hour IL-2–activated peripheral blood NK cells. Gray (4- to 10-fold) and black (>10-fold) boxes show the hypermethylated HpaII sites. E: HACE1 mRNA expression in seven NKCL cases. HACE1 mRNA expression in NKCL cases was normalized to the HACE1 expression in resting PB NK cells. Resting and 4-day IL-2–activated PB NK cells were used as the controls. The HACE1 deletion status was marked with plus and minus signs on the x axis. F: The total number of hypermethylated HpaII sites (ie, hypermethylated HpaII sites in CpG-177, CpG-88, and CpG-29 altogether) (left panel) and the number of hypermethylated HpaII sites in each CpG island compared with normal 48-hour IL-2–activated NK cells (right panel) were indicated for the same NKCL cases with the same sample order as in E. Fourfold count was set as the threshold for hypermethylation. G: MSP-qPCR results of the seven malignant NK cell lines are shown. Resting NK cells (NK0) were used as the negative, and M.SssI methylated lymphocyte DNA (Met) was used as the positive control, respectively. −ΔCt values are calculated as follows: −(CtNK cell line − CtNK0).