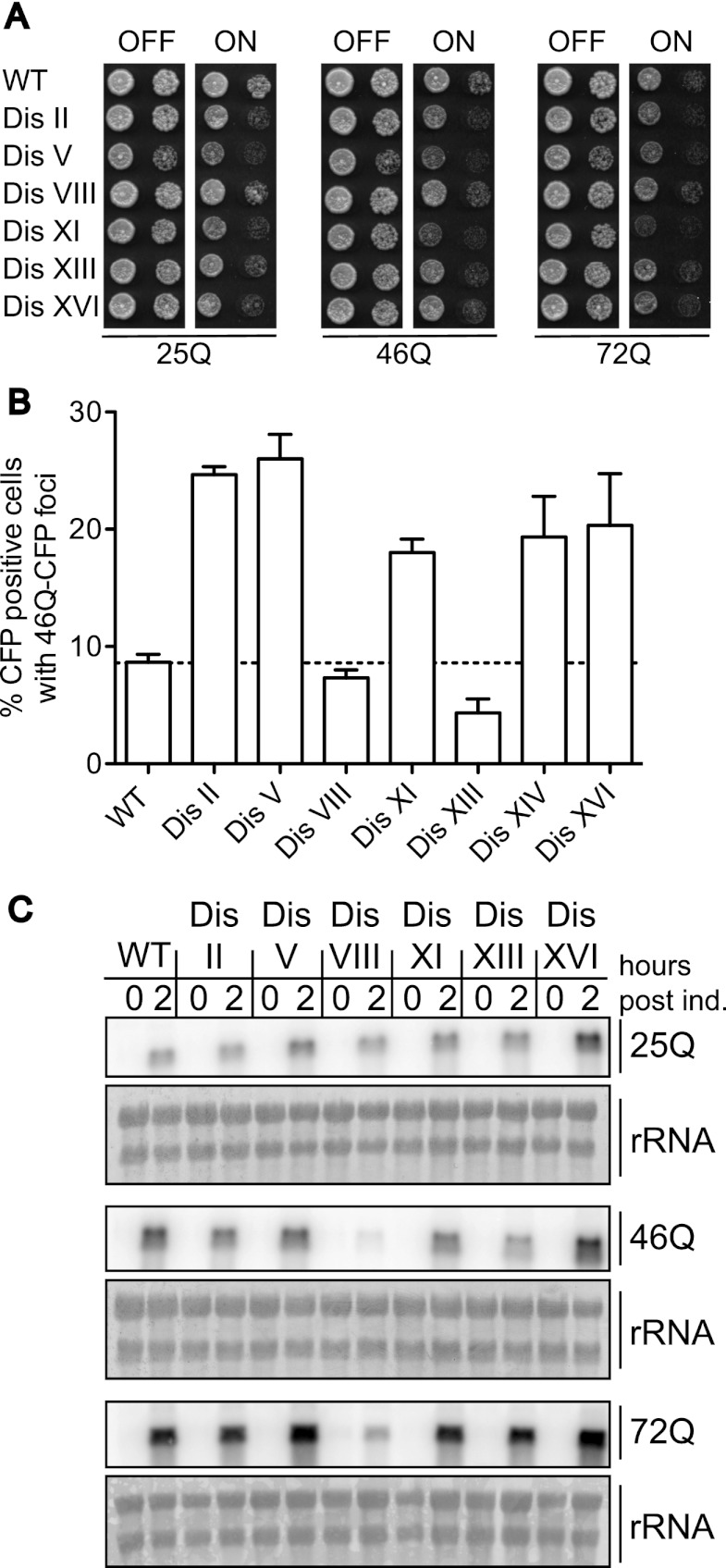
Figure 8.
Disomic yeast strains exhibit increased sensitivity to Huntingtin polyQ aggregates. (A) Wild-type (WT) and disomic strains harboring a GAL-Flag-HTT1(17AA)25QΔpro-CFP, GAL-Flag-HTT1(17AA)46QΔpro-CFP, or GAL-Flag-HTT1(17AA)72QΔpro-CFP construct were grown under conditions in which expression is repressed (YEPD) or induced (YPRG). Tenfold dilutions were plated. 25Q strains, in order, are A32114, A32115, A32116, A32117, A32118, A32119, and A32120. 46Q strains, in order, are A32121, A32122, A32123, A32124, A32125, A32126, A32127, and A32128. 72Q strains in order are A32129, A32130, A32131, A32132, A32133, A32134, and A32135. (B) Wild-type and disomic strains harboring the GAL-Flag-HTT1(17AA)46QΔpro-CFP construct were grown for 8 h in the presence of galactose to determine the percentage of cells with Htt1-46Q-CFP foci. n = 100. Shown are the mean and SEM of three independent experiments. (C) Expression of the GAL-HTT1(17aa)-Flag- nQ-CFP constructs. Strains were grown in YEP 2% raffinose to OD600 = 0.2 when 2% galactose was added. RNA was extracted from samples taken after 2 h, and the amount of HTT1-nQ-CFP RNA was determined via Northern blot analysis.