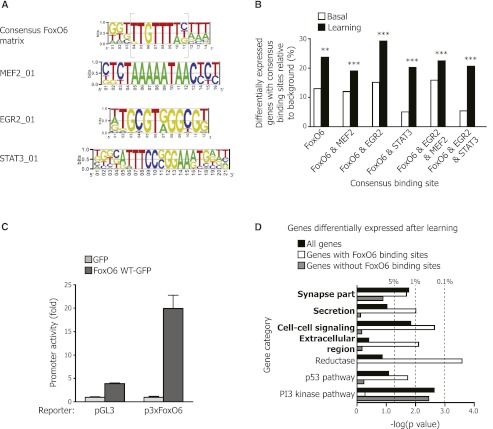
Figure 6.
The promoters of genes that are positively regulated by FoxO6 after novel object learning contain consensus binding sites for FoxO and for the activity-dependent transcription factor MEF2. (A) Consensus matrix for FoxO6-binding sites constructed by aligning the promoter sequences from the genes differentially expressed in the FoxO6 mutant and wild-type mice both in basal conditions (basal) and after object learning (learning). The known FoxO-binding site is shown in gray brackets. Consensus matrices for MEF2_01-, EGR2_01-, and STAT3_01-binding sites from the TRANSFAC database shown to co-occur with the consensus FoxO6 matrix are represented. (B) Proportion of genes down-regulated in FoxO6 mutant versus wild-type mice containing the consensus binding sites described in A in basal conditions (white bars) and after learning (black bars). (**) P < 0.01; (***) P < 0.001, log rank test. (C) The consensus FoxO6 matrix drives FoxO6-dependent transcription in cultured neurons. Luciferase assays in primary cultures of cerebellar granule neurons (CGNs) transfected with constructs expressing a control luciferase reporter (pGL3), a luciferase reporter driven by three consensus FoxO6-binding sites (p3xFoxO6), and a construct to ectopically express FoxO6-GFP. Results are normalized to renilla. Mean ± SD of a representative experiment performed in triplicate. (D) Genes regulated by FoxO6 after novel object learning and containing FoxO-binding sites are enriched for genes involved in the synapse compartment, secretion, and cell–cell signaling. All genes differentially expressed in the FoxO6 mutant mice after learning (black bars), the subset of genes containing the FoxO-binding site (white bars), or the subset of genes without a FoxO-binding site (gray bars) were compared with gene categories using DAVID version 6.7 (P < 0.05 for FoxO6 mutant vs. wild-type, one-way ANOVA). DAVID category information is presented in Supplemental Table 1. (Dashed lines) P = 0.05, P = 0.01, and P = 0.001, modified Fisher's exact test.