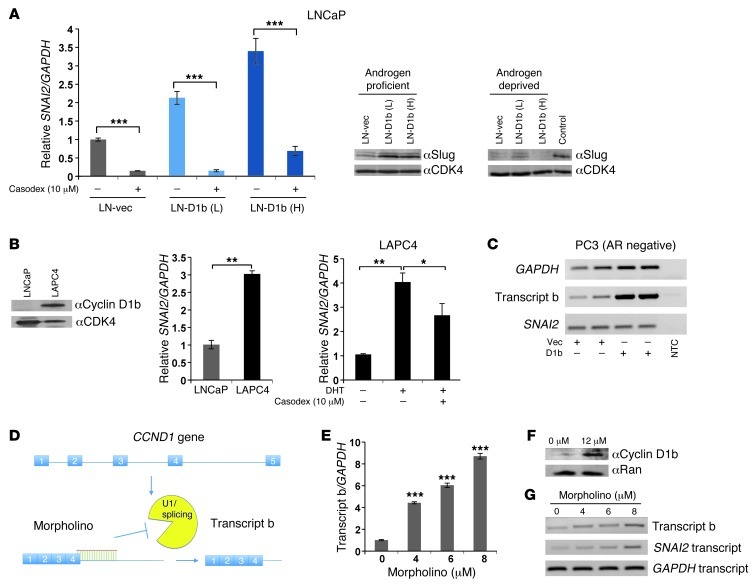
Figure 2. Cyclin D1b enhances SNAI2 (Slug) expression through cooperation with the AR axis.
(A) Left: control and cyclin D1b–expressing cells were incubated with the AR inhibitor Casodex or ethanol (EtOH) control for 24 hours, RNA harvested, and relative SNAI2 levels determined. Right: control and cyclin D1b cells were cultured in androgen-proficient or androgen-depleted conditions for 72 hours and relative levels of Slug determined. Control cells cultured in androgen-proficient medium serve as a positive control. (B) Left: LNCaP and LAPC4 cells were cultured in androgen-proficient conditions and relative expression of cyclin D1b and SNAI2 levels determined. CDK4 (protein) and GAPDH (transcript) serve as controls. Right: LAPC4 cells were hormone deprived and stimulated with EtOH (0.1%), DHT (1 nM), and/or Casodex (10 μM) for 24 hours and SNAI2 expression analyzed (normalizing to GAPDH). (C) The AR-negative cell line PC3 was transfected with cyclin D1b constructs in biological duplicate, and relative levels of transcript b and SNAI2 transcript determined. ddH2O serves as a non-template control (NTC). (D) Schematic of Morpholino mechanism of action in CCND1 alternative splicing. (E) Increasing amounts of Morpholino were introduced to LNCaP cells and relative levels of transcript b determined by qPCR after 72 hours (normalized to GAPDH). (F) LNCaP cells were treated with 12 μM Morpholino for 72 hours and levels of cyclin D1b determined. (G) Cells were treated as in E, and levels of transcript b and SNAI2 are shown. GAPDH serves as a control. Error bars represent mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.