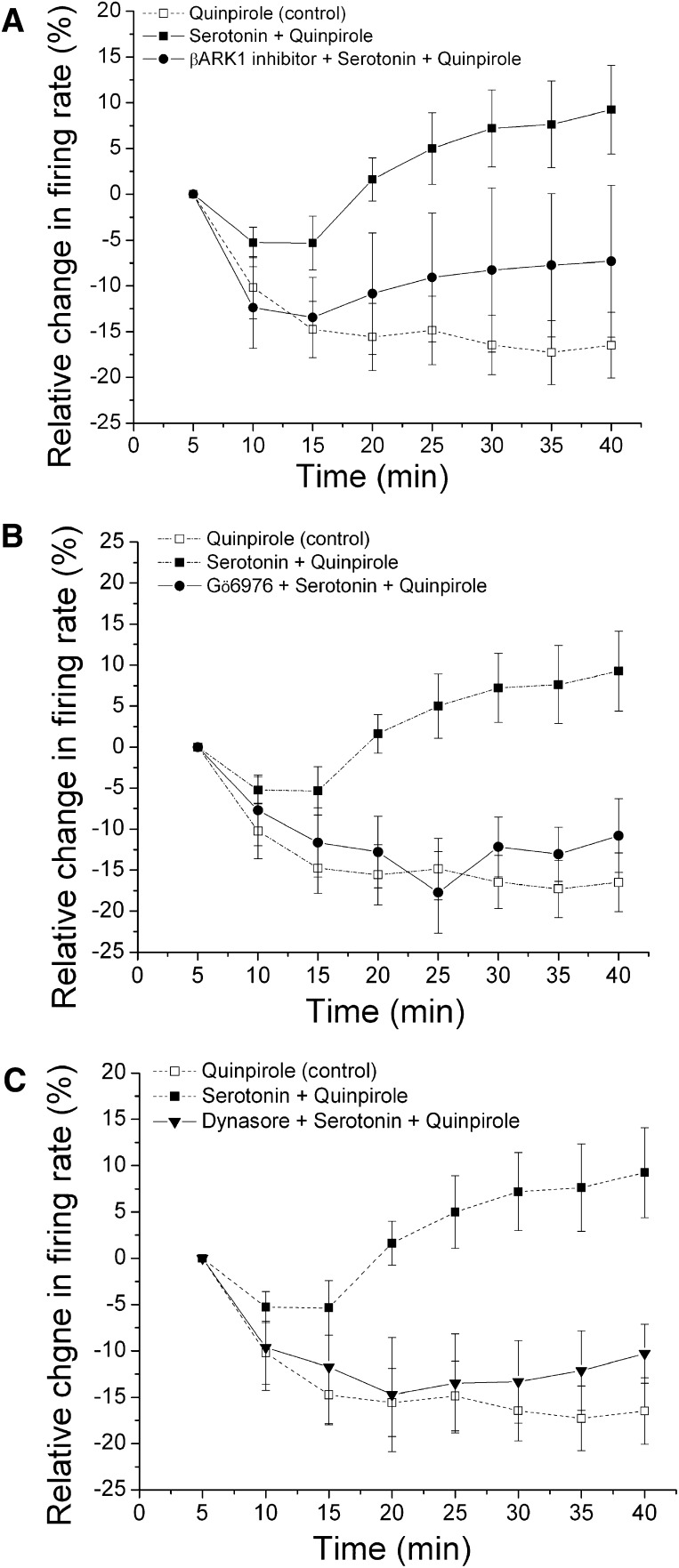
Fig. 4.
Effect of inhibitors of G protein-coupled receptor kinase-2 (GRK2), conventional protein kinase C (cPKC), and dynamin on long-duration application of serotonin (5-HT) and quinpirole. Relative change in the firing rate (mean ± S.E.M.) is plotted as a function of time. (A) effect of β-ARK1 inhibitor on long-duration application of quinpirole and 5-HT. The effect of quinpirole alone (□ and dashed line) from Fig. 3A is shown for comparison. With 50 µM 5-HT in the superfusate (▪, n = 9), there was a statistically significant difference in the magnitude of quinpirole inhibition at the 30- and 40-minute time points compared with the 10-minute time point, indicating reversal of inhibition. In the presence of 50 µM 5-HT in the superfusate and 300 μM β-ARK1 inhibitor in the recording pipette (●, n = 7), no reversal and no significant inhibition in the firing rate produced by quinpirole were observed ([quinpirole] = 72.9 ± 8.0 nM) (one-way repeated measures ANOVA, F(7,42)= 1.49, P > 0.05). (B) effect of Gö6976 on long-duration application of quinpirole and serotonin. The effect of quinpirole alone (□ and dashed line) from Fig. 3A and quinpirole in the presence of 50 μM 5-HT (▪ and dashed line) from A are shown for comparison. In the presence of 10 μM Gö6976 in the recording pipette and 5-HT in the superfusate (●, n = 6), no significant quinpirole inhibition reversal was observed ([quinpirole] = 102.5 ± 25.3 nM) (one-way repeated measures ANOVA, F(7,35)= 92.8, P < 0.05). (C) effect of dynasore on long-duration application of quinpirole and 5-HT. The effect of quinpirole alone (□ and dashed line) from Fig. 3A and quinpirole in the presence of 5-HT (▪ and dashed line) from A are shown for comparison. In the presence of 50 µM 5-HT in the superfusate and 800 µM dynasore in the recording electrode (▾, n = 6), no reversal of quinpirole-induced inhibition was observed; quinpirole (125 ± 38.7 nM) produced a statistically significant inhibition in the firing rate over time (one-way repeated measures ANOVA, F(7,35) = 4.0, P < 0.05).