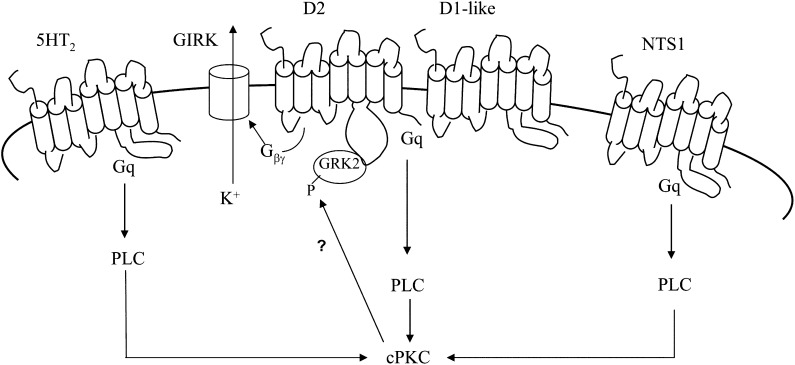
Fig. 5.
Model of the action of different Gq-coupled receptors on conventional protein kinase C (cPKC) and D2 receptor sensitivity. The diagram illustrates a hypothetical interaction of 5-HT2, neurotensin (NTS1), and dopamine (D2, D1-like) receptors on cPKC in dopamine (DA) ventral tegmental area (VTA) neurons, based on the results of our study. The G-protein coupled inwardly rectifying potassium channel (GIRK) that is activated by Gβγ and that causes the hyperpolarization resulting in a decrease in the firing rate is shown. Activation of DA receptors (D2 plus D1/D5), serotonin 5-HT2, or neurotensin NTS1 receptors activates cPKC, which phosphorylates and stimulates G protein-coupled receptor kinase-2 (GRK2). The stimulated GRK2 then phosphorylates the D2 receptor, resulting in the desensitization of the receptor.