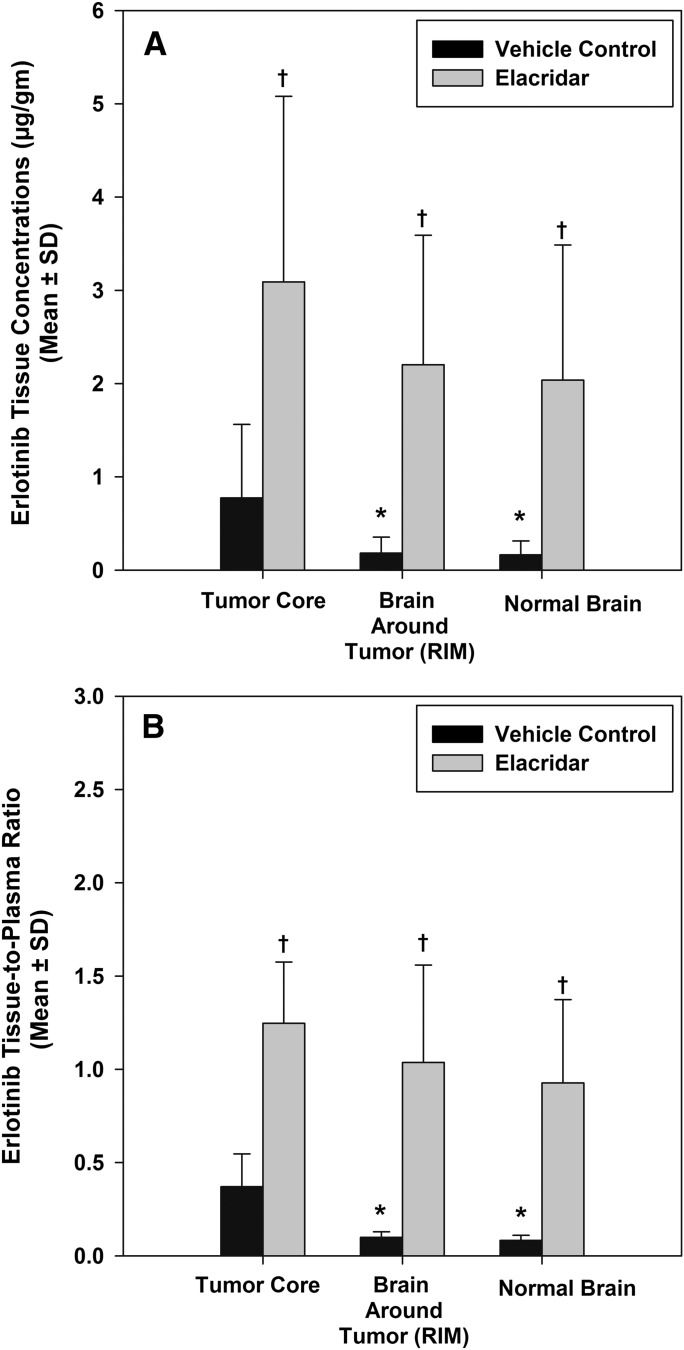
Fig. 4.
Influence of elacridar on regional distribution of erlotinib. Erlotinib concentrations (A) in the tumor core, rim, and normal brain increased significantly in the elacridar-treated group (gray bars) compared with the control (black bars). The erlotinib brain-to-plasma ratio (B) increased significantly and was approximately 1 in all three brain regions, indicating that when these two transporters are inhibited, there is no restriction of the delivery of erlotinib to the brain. This indicates that concurrent administration of a modulator of drug transporters, such as elacridar, can be used as a strategy to enhance delivery of substrate chemotherapeutic agents to the brain. The values are presented as the mean ± S.D. *P < 0.05, compared with tumor core; †P < 0.05, compared with vehicle control; n = 4 per group.