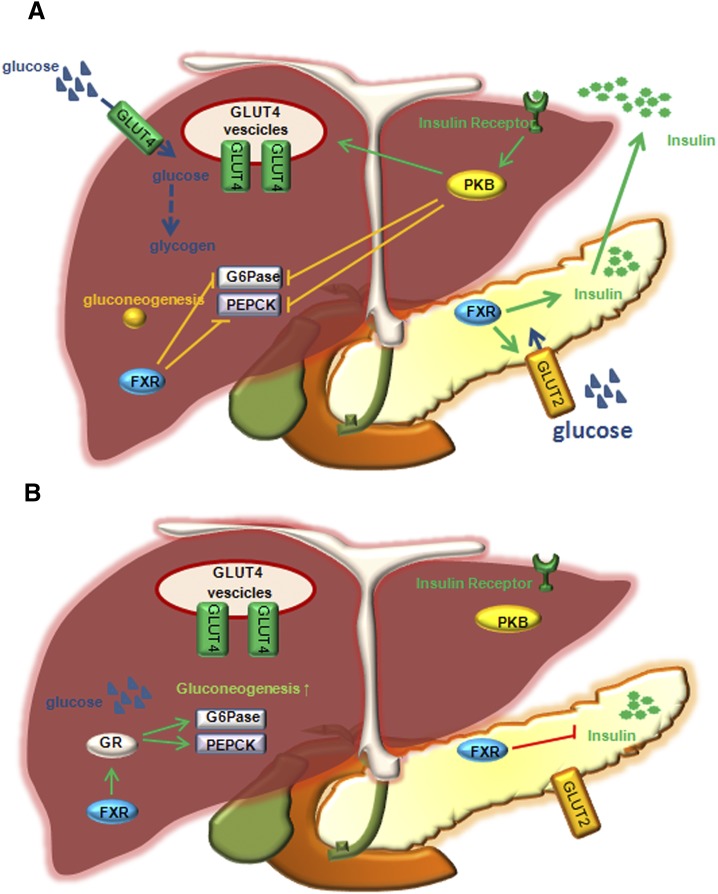
Fig. 2.
The role of FXR in regulation of glucose metabolism in mice. (A) In the fed state, insulin stimulates GLUT-4 recruitment to plasma membrane. Glucose taken up by GLUT-4 to hepatocytes stimulates glycogen synthesis. Insulin signaling activates PDZ-binding kinase, PBK, to phosphorylate and inhibit FOXO1, and results in inhibiting G6Pase and PEPCK expression and gluconeogenesis. Glucose is taken up by insulin-sensitive GLUT-2 to pancreatic β cells. FXR stimulates insulin gene transcription and secretion from β cells when glucose levels are high. (B) In the fasting state, glucagon stimulates gluconeogenesis by activating GR, which induces G6Pase and PEPCK. In addition, FXR activates GR (to stimulate G6Pase and PEPCK) and inhibits insulin gene transcription.