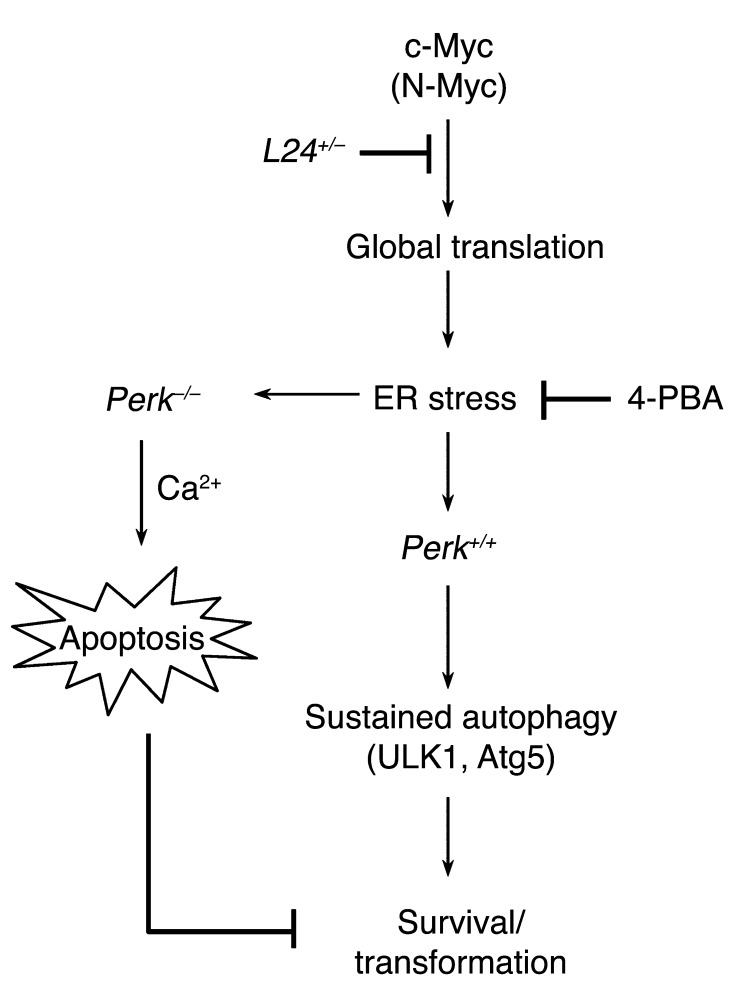
Figure 7. Model of the role of UPR activation in cytoprotection during Myc-dependent transformation.
c-Myc activation increases protein synthesis, resulting in UPR activation. This is attenuated by genetically reducing protein synthesis (L24 mouse minute) or pharmacologically increasing chaperone activity (4-PBA). In the presence of PERK, cytoprotective autophagy (LC3 processing, p62 degradation) is induced and is required for cell survival (ULK1 and Atg5 dependence). Loss of PERK results in significantly increased apoptosis, primarily through increase Ca2+ release form the ER and lack of autophagy.