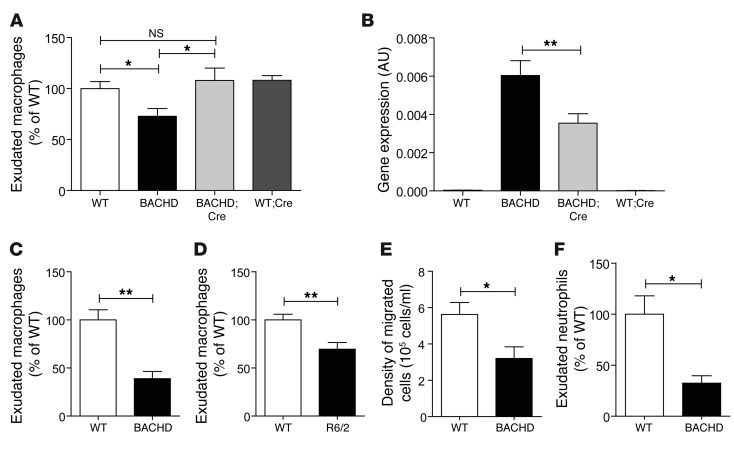
Figure 4. The migration of macrophages to the peritoneum in response to thioglycollate is defective in mouse models of HD.
Thioglycollate (3%) was injected into the peritoneum of HD mice, and cells were harvested after 24 or 48 hours. (A) At 6–9 weeks, BACHD mice have a marked reduction in peritoneal macrophage recruitment. This defect was completely normalized in BACHDTg/+;CD11b-Cre (BACHD;Cre) mice, in which mutant htt expression is absent in CD11b-expressing cells. Values are mean ± SEM. n = 20, 14, 7, and 15 for WT, BACHD, BACHDTg/+;CD11b-Cre, and WT;CD11b-Cre (WT;Cre), respectively. *P < 0.05 (1-way ANOVA, Bonferroni’s post hoc test). (B) Mutant Htt gene expression is decreased in peritoneal exudates from BACHDTg/+;CD11b-Cre mice compared with BACHD. Values are mean ± SEM. n > 3. **P < 0.01 (1-way ANOVA, Bonferroni’s post hoc test). (C and D) Macrophage recruitment was also decreased in (C) BACHD at 8–10 months (WT, n = 3; BACHD, n = 5) and (D) R6/2 mice at 8 weeks (WT, n = 16; R6/2, n = 15). For evaluation of macrophage recruitment, cells were stained with anti-F4/80–APC and analyzed by FACS. Recruited populations were expressed as the percentage of F4/80dim cells to total cells. (E and F) The density of total infiltrating cells (E) and exudate neutrophils (Gr-1+ cells within the CD11b population) (F) is also lower in BACHD mice than in controls. Results are normalized to WT controls. Values are mean ± SEM, n = 6–18. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 (t test). n represents number of mice used.