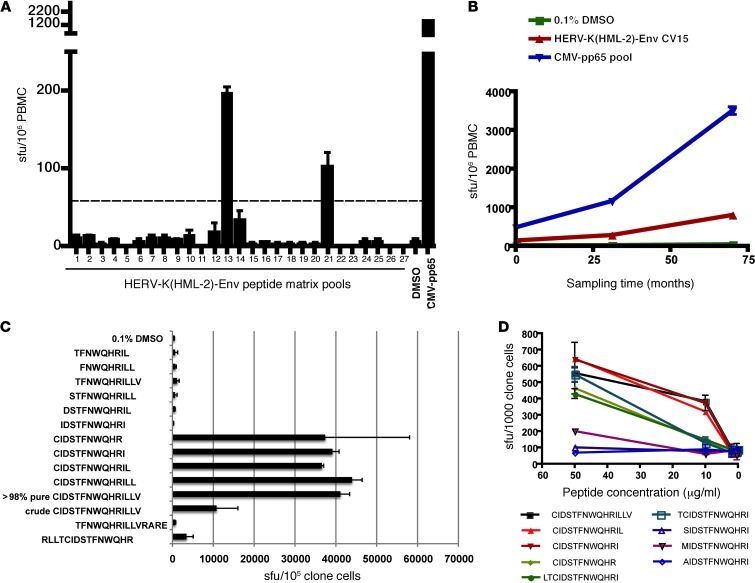
Figure 3. Identification of a HERV-K(HML-2)-Env–specific CD8+ T cell response and fine mapping of the T cell determinant.
(A and B) IFN-γ ELISPOT was performed on PBMCs from the HIV-1–infected elite controller OM9. Results depicting mean sfu per 106 PBMCs, with error bars representing standard deviation, are shown. (A) All tests were performed in duplicate. The dashed line represents the threshold for a positive response as defined by meeting the criteria of >3x background and >50 sfu per million PBMCs after background subtraction. (B) All tests were performed in quadruplicate. (C and D) IFN-γ ELISPOT was performed on a HERV-K(HML-2)-Env–specific CD8+ T cell clone from OM9. (C) The specificity of the HERV-K(HML-2)-Env–specific clone was confirmed using the original CIDSTFNWQHRILLV peptide (crude) and a newly synthesized batch of the same peptide (>98% pure) and fine mapped using a panel of truncated peptides. IFN-γ ELISPOT data depicting mean spots per 106 clone cells (tested in duplicate), with error bars representing standard deviation, are shown. (D) The reactivity of the HERV-K(HML-2)-Env–specific T cell clone to serial dilutions of the indicated peptides was tested in the presence of autologous BLCLs. Tests were performed in triplicate, and error bars represent SEM.