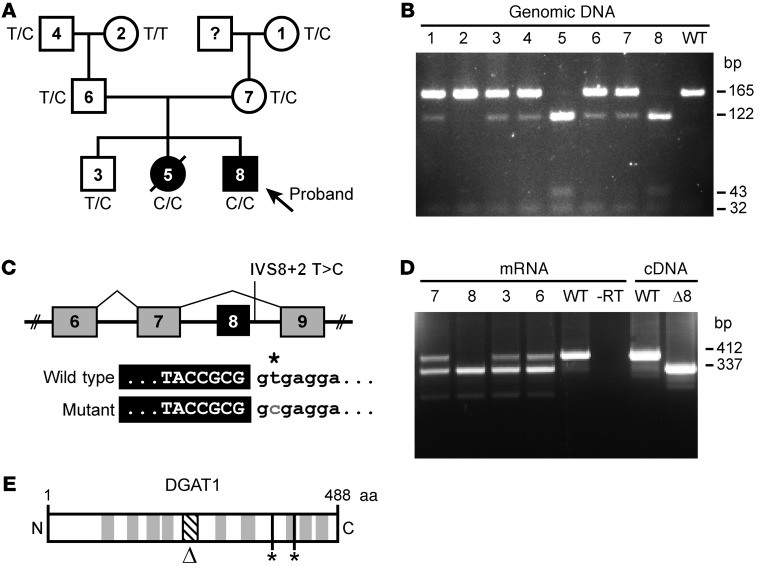
Figure 1. Mutation in DGAT1 segregates with CDD.
(A) Pedigree of the affected family, indicating diarrheal phenotype and DGAT1 genotype. T, wild type; C, mutant. (B) RFLP assay of genomic DNA confirming mutation presence. PCR product digested with Fnu4HI yields 165 and 32 bp for reference and 122, 43, and 32 bp for mutant allele. Numbers refer to the family members indicated in A. (C) Predicted splicing patterns for wild-type and mutant alleles. (D) RT-PCR analysis of mRNA from blood of the proband, unaffected sibling, and parents. Numbers refer to exons. The asterisk indicates the mutated nucleotide (“T” for wild type and “C” for the mutant allele). Mutant DGAT1 allele yields Δ8 mRNA. Numbers refer to the family members indicated in A. (E) DGAT1 protein diagram showing predicted transmembrane domains (gray), putative catalytic residues (*), and Δ8 region (Δ, diagonal lines).