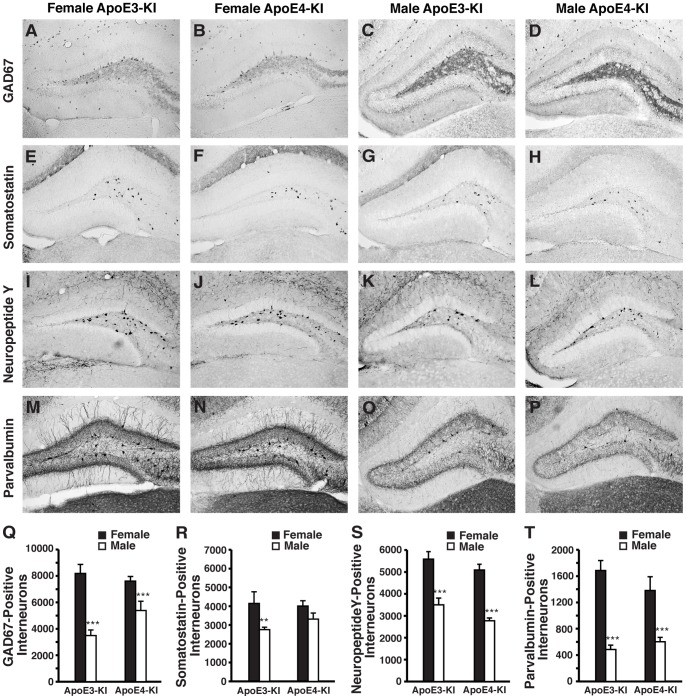
Figure 2. ApoE-KI mice exhibit basal sex differences in hilar GABAergic interneurons at 1-month of age.
A–D, Representative images (200x) of anti-GAD67-immunostained sections of the hilus of female apoE3-KI (A), female apoE4-KI (B), male apoE3-KI (C), and male apoE4-KI (D) mice at 1 month of age. E–H, Representative images (200x) of anti-somatostatin-immunostained sections of the hilus of female apoE3-KI (E), female apoE4-KI (F), male apoE3-KI (G), and male apoE4-KI (H) mice at 1 month of age. I–L, Representative images (200x) of anti-NPY-immunostained sections of the hilus of female apoE3-KI (I), female apoE4-KI (J), male apoE3-KI (K), and male apoE4-KI (L) mice at 1 month of age. M–P, Representative images (200x) of anti-parvalbumin-immunostained sections of the hilus of female apoE3-KI (M), female apoE4-KI (N), male apoE3-KI (O), and male apoE4-KI (P) mice at 1 month of age. Q–T, Quantification of hilar GABAergic interneurons positive for GAD67 (Q), somatostatin (R), neuropeptide Y (S), or parvalbumin (T) in female and male apoE-KI mice at 1 month of age (n = 6–12 per group). Results in histograms are presented as the total number of positive cells counted per brain. Male apoE-KI mice have significantly fewer hilar GABAergic interneurons than female apoE-KI mice at 1 month of age by t-test, **p<0.01; ***p<0.001.