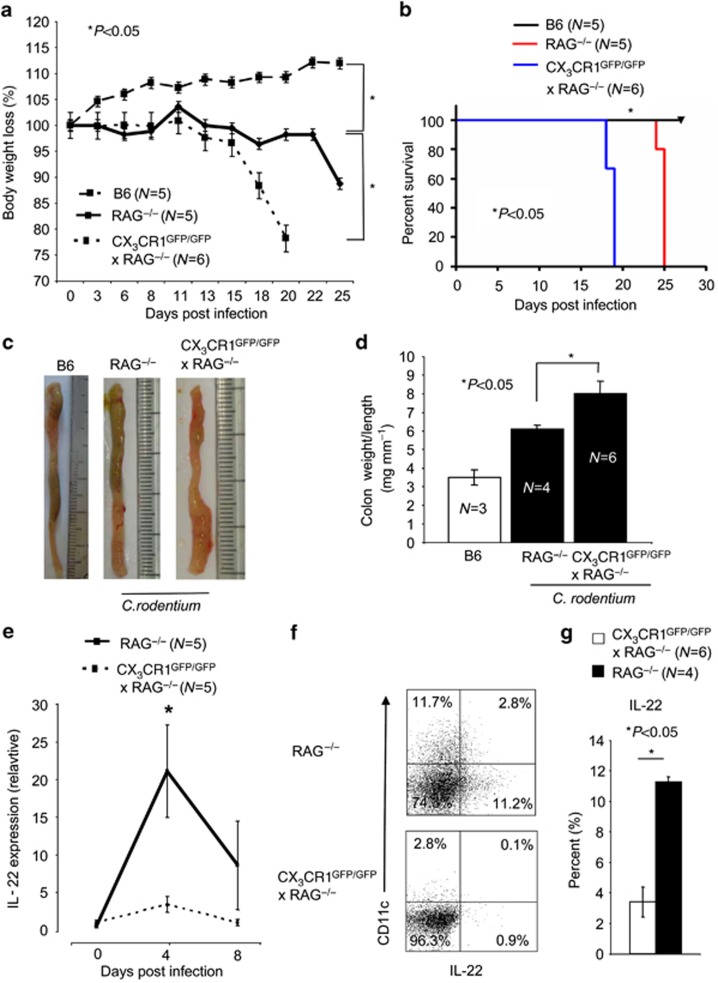
Figure 4.
Recombination-activating gene (RAG)−/− mice lacking CX3CR1 develop a rapid Citrobacter rodentium infection. (a) RAG−/− × CX3CR1GFP/GFP and RAG−/− mice were infected with 2 × 109 C. rodentium. Mean±s.e.m. loss of body weight (%) per group is shown for the indicated animals. P-values were calculated with a nonparametric Student's t-test; P<0.05 was considered statistically significant. (b) Survival of RAG−/− × CX3CR1GFP/GFP and RAG−/− infected with 2 × 109 C. rodentium is shown. (c) Colons were removed at the end of the experiment and representative colons of the indicated groups are shown. (d) The colon weight and length was determined and expressed as colon weight/length ratios. In the nonparametric Student's t-test, P<0.05 was considered statistically significant. (e) Interleukin (IL)-22 expression in the proximal colon of infected RAG−/− and RAG−/− × CX3CR1GFP/GFP animals was analyzed by quantitative real-time PCR. β-actin was used as housekeeping gene to normalize cDNA input between samples. Normalized ct-values of the noninfected samples (baseline) are set to 1 and values are plotted as fold expression of the baseline (f) IL-22 expression by colonic lamina propria (cLP) cell isolates from C. rodentium-infected RAG−/−, (age- and sex-matched) and RAG−/− × CX3CR1GFP/GFP animals was analyzed by multicolor flow cytometry. Numbers indicate the percentage of IL-22-positive cells. (g) Mean (±s.e.m.) percentage of IL-22+ cells isolated from the cLP of C. rodentium-infected B6, (age- and sex-matched), and CX3CR1GFP/+ and CX3CR1GFP/GFP animals is shown. In the nonparametric Student's t-test, P<0.05 was considered statistically significant (*P<0.05).